Defending the Modern Identity Stack: Scattered Spider and the New Era of Identity Warfare
Why Identity, SaaS, and Cloud Now Define the Modern Attack Surface and How Leading Vendors Are Detecting and Responding to Scattered Spider (LUCR-3)
Today’s Report Structure
SACR has a broad thesis that identity security is becoming one of the biggest opportunities in cybersecurity. Over the upcoming weeks, you’ll see more reports from our team. Today, we’re introducing a new report style that looks directly at cybercriminals and the methods they use to breach organizations.
Organizations today are facing a rapid escalation in identity-centric threats driven by highly capable, financially motivated adversaries. Among the most disruptive is Scattered Spider (UNC3944/Octo Tempest), a cybercrime group whose tactics reflect a clear shift in how modern intrusions unfold. Their operations blend expert-level social engineering, targeted abuse of identity systems, and rapid movement across cloud environments that can overwhelm traditional security architectures in hours rather than days.
This report provides a clear, structured view of the threat landscape surrounding Scattered Spider and similar actor groups. It outlines how these attackers gain initial access, how they exploit weaknesses across identity, SaaS, cloud, and on-prem environments, and why current defenses often fail. More importantly, it distills what CISOs need to prioritize from identity visibility and posture hardening to behavioral detection, so that organizations can materially reduce their exposure to identity-based attacks. Beyond the threat analysis, this report also examines the emerging defensive ecosystem built to counter these adversaries; we highlight capabilities around Identity threat detection, SaaS posture management, automated identity verification, and graph-based analytics that are reshaping how enterprises protect themselves.
To ground this landscape in real-world capabilities, this report features solution profiles from:
Silverfort
Permiso
CrowdStrike
These vendors were selected as representative examples of the different approaches being taken across the identity and threat-detection ecosystem. Their appearance in this report is not exclusive; many vendors contribute meaningfully to this space, but their capabilities provide clear, practical insight into how the industry is evolving.
We hope you find value broadly from the attack analysis in this report and give your feedback if you enjoy this style of cyber reports!
Actionable Summary
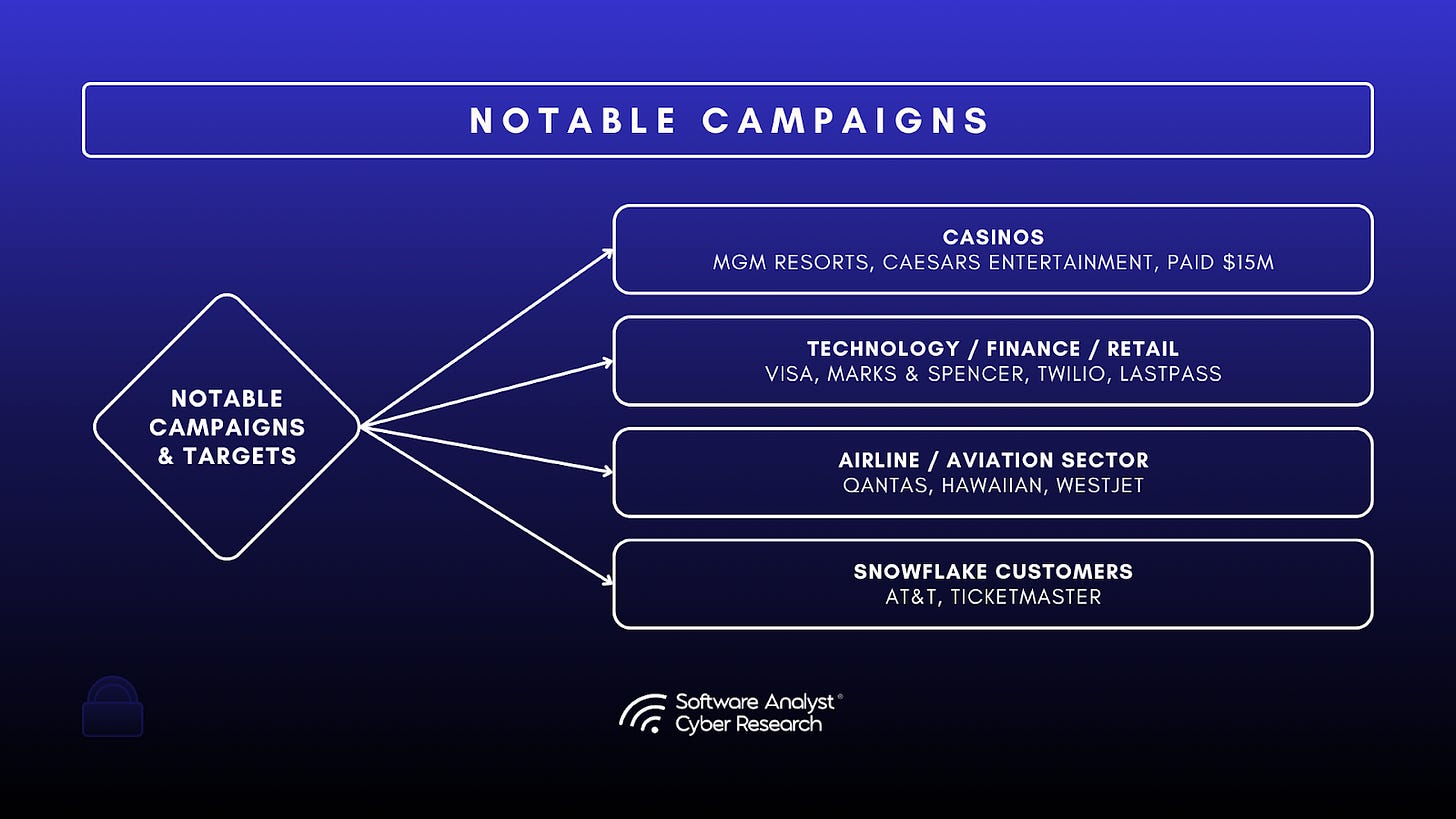
Scattered Spider, also tracked under numerous aliases such as LUCR-3, UNC3944, Octo Tempest, Muddled Libra, and Oktapus, is an exceptionally aggressive and financially motivated Cyber crime group that became active around May 2022. The collective consists largely of young, native English-speaking individuals primarily based in the United States and the United Kingdom. The group’s core strength lies not in technical exploits but in its expert mastery of social engineering, specifically voice phishing (vishing), which they leverage to exploit human trust within corporate systems. The group has targeted large enterprises across essential sectors including hospitality, finance, retail, and aviation, resulting in estimated losses in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
The group’s primary initial access method involves impersonating high-value employees to manipulate IT help desk staff into resetting passwords or, critically, re-enrolling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to an attacker-controlled device, thereby bypassing critical security controls. They are known to regularly coordinate over telegram and discord channels as well as underground forums, to focus on and pivot strategies to breach a target. Once inside a victim’s network, Scattered Spider demonstrates a rapid operational tempo, utilizing Living Off the Land (LOTL) tactics, security tools and remote access software if they can compromise them and deploy legitimate remote monitoring and management (RMM) software or use endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools for persistence and lateral movement.
Bottom Line for CISOs
To defeat threat actors like Scattered Spider, organizations need to employ greater identity visibility, intelligence focused tools, upgraded authentication lik ki ise phishing resistant passkeys and enhanced ability to perform identity-based threat detection and response and universal security posture assessment.
Typical Threat Actor Phases
Scattered Spider is also known by many names and has many affiliate groups
Key Attack Phase Considerations
Evolving Attack Vectors
Scattered Spider (also known as UNC3944, Roasted 0ktapus, STORM-0875, and Octo Tempest) utilizes a range of sophisticated attack techniques, including SIM swapping, push fatigue with MFA push through Identity Providers (IdPs), and credential harvesting via infostealers, ransom data breaches, IaaS and SaaS applications. Their recent activity has focused on cloud environments and VMware ESXi infrastructure. Scattered spider’s strategy employs social engineering, credential abuse, MFA compromise and massive data exfiltration for their extortion and high-tier ransomware variants.
Rapid On-Premise Pivot
A critical take away is the speed and multi-lateral pivots that this threat actor has performed. The group’s high operational tempo and continuous pivoting across tactics and targets are notable with breadth, scale and their brazenness to attack very publicly known entities. The group, composed primarily of young, native English speakers, quickly evolved from simple SIM swapping and phishing to sophisticated, multimillion-dollar extortion. Once they achieve initial access, their attacks are fast and furious, requiring defenders to respond within well under 48 hours before encryption is executed. Tactically, the group constantly pivots: they recently abandoned phishing pages to rely exclusively on vishing (voice phishing) against IT help desk staff as their primary initial access method. They are capable of adapting their intrusion methods in real-time by monitoring internal corporate communications for security discussions. Managed Service Providers (MSPs) as a single point of entry to reach multiple victim networks.
Cloud-Focused Attacks
Scattered Spider demonstrates multi-lateral pivots by routinely changing their infrastructure and domain patterns every one to two months, and by strategically shifting alliances between major ransomware affiliates, including ALPHV/BlackCat, Qilin, and DragonForce. These attackers moved from initial access to on-premise environments rapidly, probably because of use of more traditional (and perception of where more sensitive data may be), often leveraging Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) and Virtual Private Networks (VPN) exploiting vulnerabilities in ESXi, extracting drive images and then carving files to extract information from files like NTDS.dit. There’s a significant focus of this threat actor on cloud environments, especially Amazon Web Services (AWS), where the attackers have used the AWS Management Console, S3 Browser, and Cloudshell for enumeration of the environment, credential harvesting, instance profile replacement, and disabling security measures like GuardDuty and to stop logging for S3 data theft.
Social Engineering:
Social engineering tactics have long been a mainstay fallback for threat actors wanting to gain access, but in recent years become a first-step, especially with Scattered Spider, where they recently abandoned phishing pages to rely exclusively on vishing (voice phishing) against IT help desk staff as their primary initial access method. The threat actors involved are capable of adapting their intrusion methods in real-time by monitoring internal corporate communications for security discussions. They actively seek discussions and keywords by using both automated and manual methods of discovery, then adjusting their focus on calling up the Direct helpdesk (often as a Chief Financial Officer (CFO), likely due to the role being empowered with privilege and closer to money. Then using social engineering as a prominent tactic, with attackers using personas of high-level IT personnel they compromise.
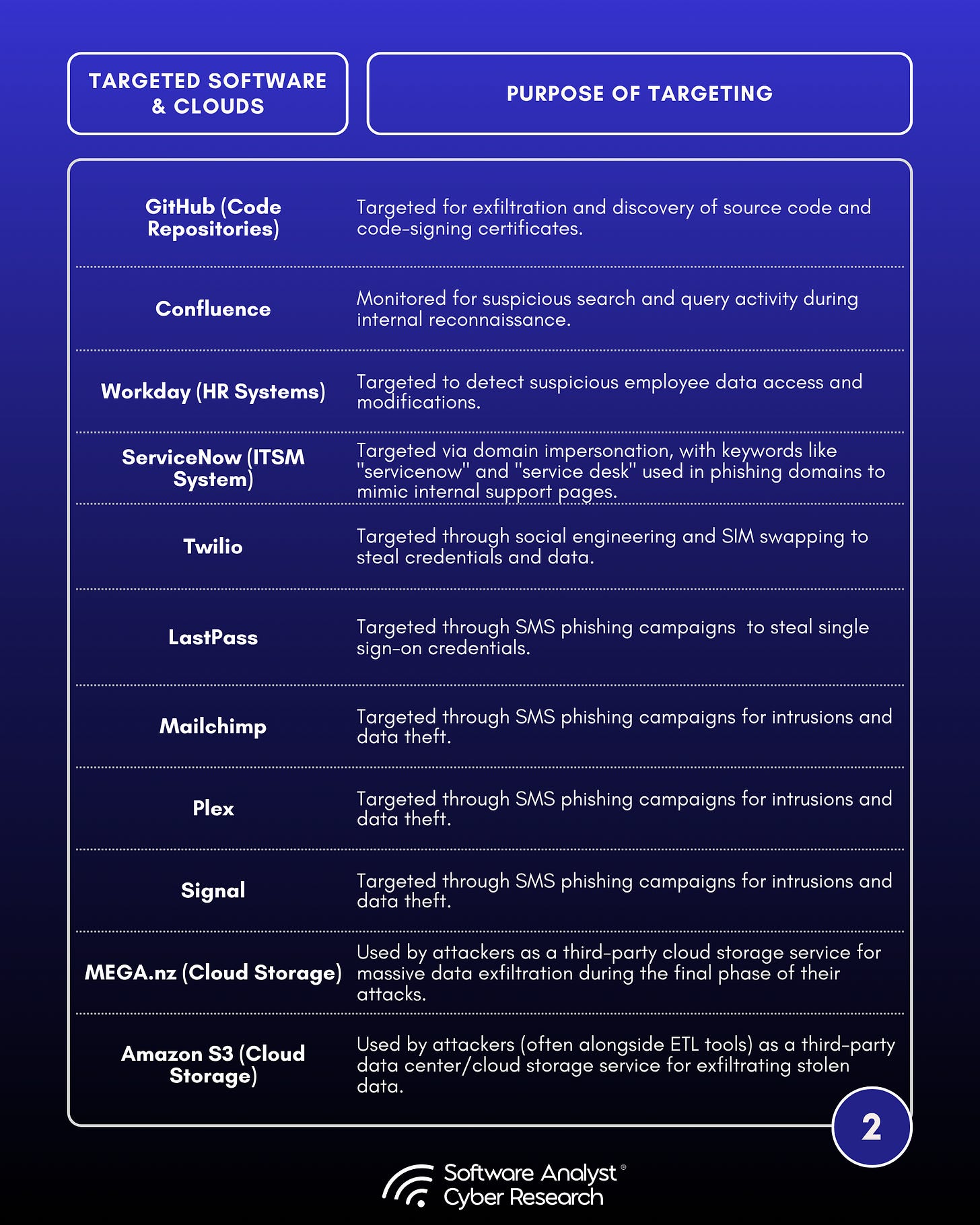
Reconnaissance in SaaS Applications:
Scattered spider attackers often perform extensive reconnaissance in SaaS applications to understand the environment and facilitate credential harvesting. Below is a list of common SaaS applications they target.
Notable Campaigns
Common SaaS Applications Scattered Spider Targets
What should organizations do to thwart, mitigate and respond to Scattered Spider?
Although every security product may have some contribution to detection and response, CISOs need to focus on tools that matter most. Below is a framework for thinking about various aspects of the Scattered Spider attacks thus far, and the most well aligned tools to help with mitigating this threat actor and their adjacent affiliates.
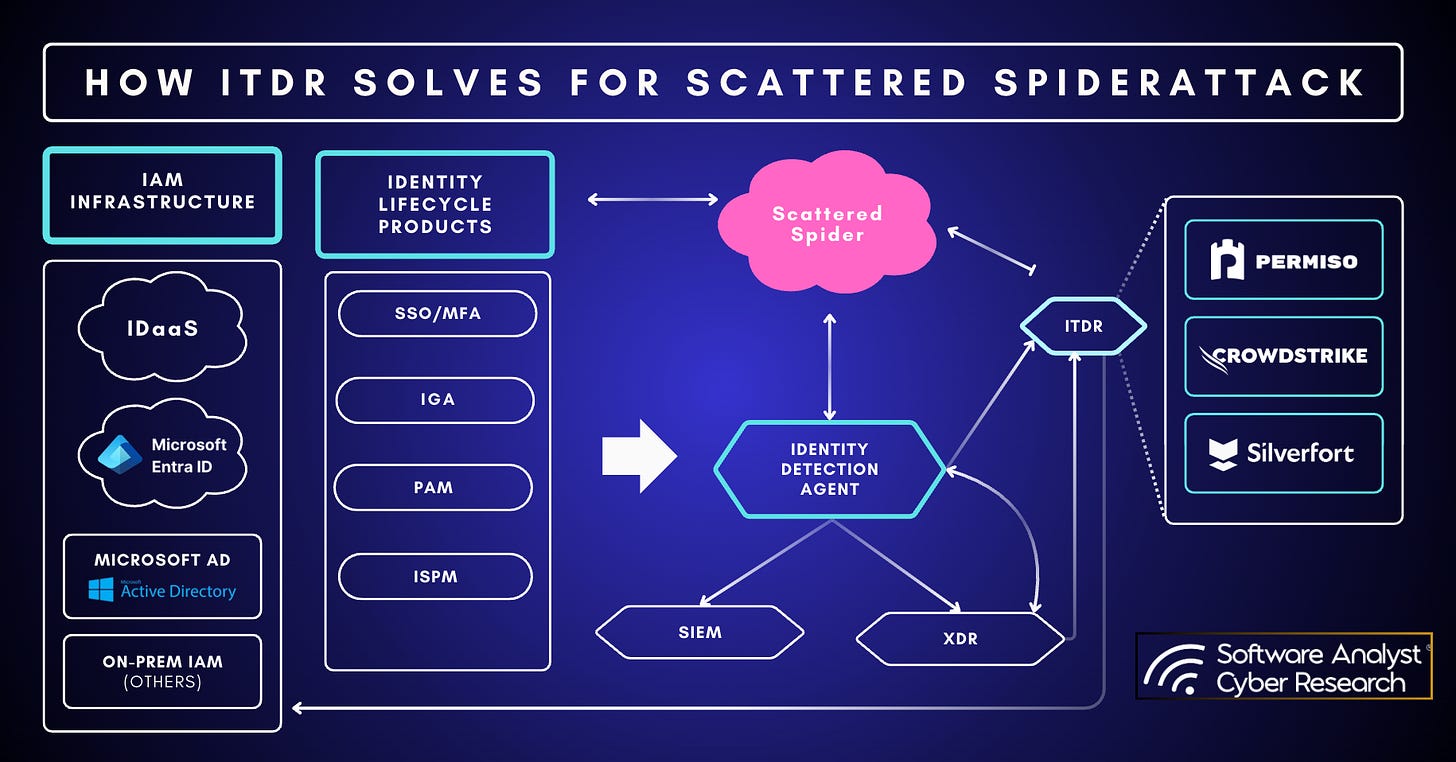
How tools are evolving to help address Scattered Spider?
The defense posture against sophisticated threats like Scattered Spider has fundamentally shifted, moving beyond the limitations of traditional perimeter defenses to integrated identity and SaaS posture assessment, intelligence collection with graph analytics and detection and response against identity and credential threats. This is because identity systems and human vulnerability (especially in social engineering like vishing and phishing) are now the primary attack surface and easiest to execute responses with, the cybersecurity market is evolving rapidly. Threats like Scattered Spider necessitate hardening organizational processes, ensuring end to end testing of processes is performed, with an enhanced focus on validation of voice and video interactions as well. Organizations must use new identity visibility intelligence platforms and identity threat detection and response technologies to enhance security outcomes. This is driving the emergence and maturation of specialized tool categories.
CISO Preparation and Response Framework
CISO’s must prioritize Comprehensive Identity Visibility (Discover):
Complete Inventory:
Implement solutions to discover all identities (human, machine, API Keys, AI, vendor) across all environments (IdPs, SaaS, Cloud, On-Prem) and stitch them into a comprehensive view of risk and access (entitlements).
Identity Classification:
Classify identities to understand their nature (human, non-human, vendor, AI-based) and map the architecture of the identity fabric.
Universal (End to End) Identity Stitching and Visibility:
Track identities end to end, throughout their entire sessions, from IdPs (e.g., Okta) to cloud deployments (AWS, GCP, Azure) and SaaS applications (Salesforce, Slack, Notion).
CISOs Must Prioritize Identity Posture Hardening (Protect):
Configuration & Exposure Audits:
Continuously scan cloud and identity configurations for weaknesses such as missing MFA, broad roles, unconstrained access, and insecure API keys.
Reduce Excess Privileges:
Minimize the attack surface by limiting credential compromise, thwarting insider threats, just-in-time privileged access and eliminating privilege creep.
Prioritized Remediation:
Utilize threat-informed risk modeling to prioritize fixes, focusing efforts on identities and misconfigurations most likely to be targeted by attackers.
CISOs must Leverage Behavior-Based Threat Detection (Defend):
Runtime-Based Approach:
Detect access anomalies coupled with significant environmental changes to identify malicious threat actors during their operations.
Behavior Monitoring:
Baseline normal identity behavior to detect anomalies like impossible travel logins or unusual data downloads that may indicate compromise.
Cross-System Correlation:
Aggregate telemetry from endpoint, cloud, SaaS, and identity systems to correlate events tied to an identity into multi-plane alerts.
Advanced Detection Signals:
Leverage advanced, research-driven rules (for example the 1,500+ from Permiso’s P0 Labs) to defend against account takeover, credential theft, insider abuse, and emerging threats.
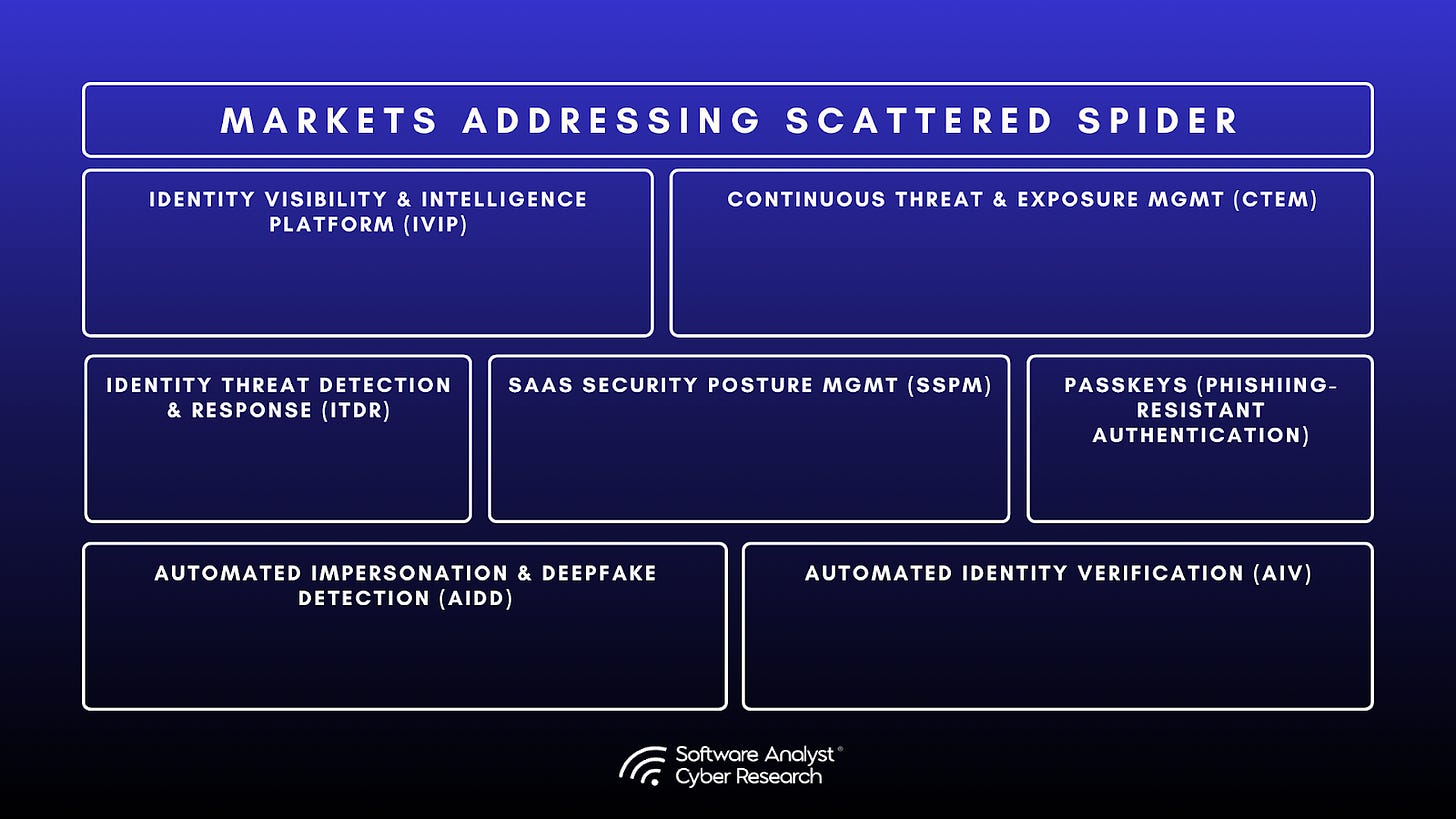
Emerging Technologies
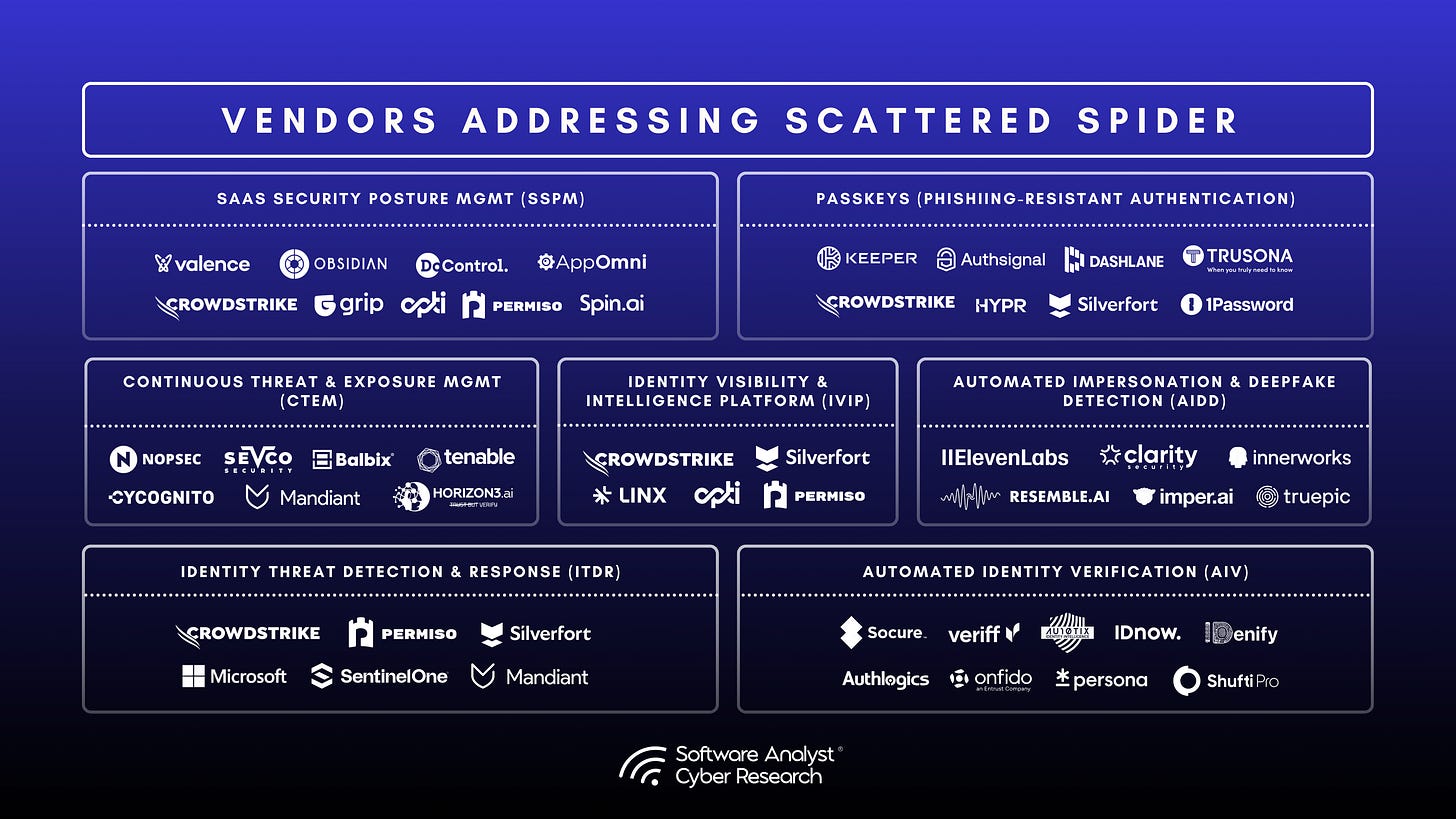
Below is a landscape view of vendors that work to address the elements surrounding new methods of detection, hygiene, posture, and validation that are applicable to Scattered Spider. With early emerging technologies with a focus on Identity Intelligence and Automated Impersonation Detection (behavioral identity, device and content detection) approaches.
How the Industry is Responding
A critical development is the rise of Automated Identity Verification (AIV) platforms. These solutions move beyond manual, often inconsistent, verification processes at points of access (like the IT help desk or self-service password resets). AIV platforms implement robust, policy-driven workflows designed to replace human discretion with standardized, automated checks. This directly counters Scattered Spider’s reliance on social engineering for initial access, neutralizing signature-based vishing and phishing attempts at the crucial pre-logon or initial authentication stage.
Because of the ineffectiveness of traditional SMS 2FA and push notifications against determined attackers like Scattered Spider, vendors are focusing on technologies such as FIDO2 (WebAuthn, CTAP) authenticators and PKI-based MFA. Organizations are now prioritizing more phishing-resistant Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) solutions that offer stronger authentication methods like MFA passkeys, which tie users more to their devices leveraging cryptographically tied fingerprinting. These offer cryptographic strength and are significantly harder for attackers to bypass or spoof, providing a much-needed layer of defense against credential theft.
To keep pace with the adversary’s rapid operational tempo and complex attack chain, the industry is increasingly adopting continuous security validation with posture assessment tools, often leveraging Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS) or Continuous Exposure Management (CTEM) tools to explore their external environments and clouds. These tools often help simulate not just generic attacks, but specific adversary TTPs (like Scattered Spider’s) throughout the kill chain – from initial infiltration via social engineering to stealthy Living Off the Land (LOTL) techniques for lateral movement and persistence. The move to constant, proactive testing allows organizations to continuously measure their security posture, identify unknown vulnerabilities, and accelerate remediation before an attacker can exploit them.
Security operations teams are changing and are increasingly leveraging advanced Agentic AI tools to analyze identity and entitlements, and visualize, investigate and perform detections on data originating from SaaS and Cloud, enabled by graph databases and graph based views of identity information, along with analytics of related events. Emerging AI systems and agentic security solutions can ingest vast amounts of security telemetry from diverse sources, including cloud environments and virtualized infrastructures like VMware ESXi or security data pipeline platform (SDPP) tools. Leading tools possess the capability to autonomously analyze complex threat patterns, prioritize alerts, and even orchestrate response actions. This dramatically reduces the Mean Time to Contain (MTTC), transforming containment from hours or days to mere minutes.
Although many tools and organizations like Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) are involved, the primary organizations that have been responsible for tracking and responding to the highly impactful cybercrime group Scattered Spider are a collaboration between major cybersecurity firms and government agencies. In the private sector efforts from CrowdStrike (which named the group), Microsoft, and Mandiant (Google Cloud), and Permiso have been involved, all of whom specialize in incident response and monitoring the actor’s sophisticated tactics, including social engineering, identity compromise, and cloud platform targeting.
Key Solutions CISOs Should Implement to Address This Threat
Phishing-Resistant Authentication (e.g., FIDO2/Passkey technology)
Help Desk Account Recovery and Identity Verification (IDV) Solutions
Identity Visibility & Intelligence Platform (IVIP)
Cloud Identity Entitlement Management (CIEM)
Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)
SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM)
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM)
Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP)
Modernized Privileged Access Management (PAM) (focused on just-in-time access)
Zero Trust Identities and Access Solutions
Continuous Threat and Exposure Management (CTEM)
Select Vendor Profiles
Below, we profile select vendors addressing the needs of organizations desiring the ability to detect Scattered Spider. This is only a sampling of providers, use cases and their abilities to Discover, Protect and Defend against these types of threats. This is not an exhaustive list of vendors.
Permiso
The Permiso Identity Security Platform unifies and secures organizations’ modern identity attack surface across all identity types and environments, directly addressing threats posed by groups like Scattered Spider.
Permiso Identity Graph: The core of the Permiso platform is its Universal Identity Graph, which provides comprehensive visibility and classification of all identities and their associated behavior. This is crucial for identifying the various AKAs (SCATTERED SPIDER, UNC3944, Roasted 0ktapus, STORM-0875) and their activities.
Discovery Capabilities
Comprehensive Identity Visibility: Permiso provides a complete inventory of all identities across environments, stitching them into a unified view of risk and access. This counters attackers’ ability to exploit unknown or unmonitored identities and minimizes the effects of identity drift.
Identity Classification: By classifying identities (human, machine, AI, vendor), Permiso exposes the architecture of an identity fabric, making it harder for attackers to blend in or exploit the unique traits of different identity types.
Universal Identity Stitching: Permiso tracks identities through their sessions, from IdPs to cloud deployments and SaaS apps, providing end-to-end visibility and clear relationship maps across identity types. This is essential for detecting and limiting the lateral movement and credential harvesting tactics used by Scattered Spider.
Protection Capabilities
Identity Posture Hardening: Permiso continuously scans cloud and identity configurations to find weaknesses such as missing MFA, overly broad roles, unconstrained access, and insecure API keys, vulnerabilities which are often exploited in initial access and privilege escalation by Scattered Spider.
Reduce Excess Privileges: By minimizing the attack surface and limiting credential compromise, Permiso directly addresses the threat of credential harvesting and insider threats, while reducing the blast radius of potential attacks.
Prioritized Remediation: Permiso uses threat-informed risk modeling to prioritize fixes, focusing efforts on the identities and misconfigurations most likely to be targeted by groups like Scattered Spider.
Defend Capabilities:
Behavior-Based Threat Detection: Permiso’s runtime-based approach establishes a behavioral baseline, enabling detections of access anomalies and significant environmental changes. Permiso then alerts organizations to malicious threat actors as they operate, even during rapid on-premise pivots.
Behavior Monitoring: By baselining normal identity behavior, Permiso detects anomalies such as impossible travel logins or rare data downloads, which are indicators of compromise often associated with Scattered Spider’s activities.
Cross-System Correlation: Permiso aggregates telemetry from cloud, SaaS, and identity systems to correlate events tied to an identity into high-fidelity multi-plane alerts. These alerts provide a holistic view of an attack timeline across different environments, identity types, and behaviors; which is necessary to stop groups like Scattered Spider from rapidly jumping around an environment.
Advanced Detection Signals: With over 1,500 cutting-edge, research-driven rules from Permiso’s P0 Labs, organizations can defend against account takeover, credential theft, insider abuse, and emerging threats employed by Scattered Spider. P0 Labs has published multiple open-source tools to help the security community address sophisticated threat actors like Scattered Spider.
Silverfort
The Silverfort Identity Security Platform is a unified solution designed to discover, protect, and defend all human, non-human, and AI agent identities across on-prem, hybrid and multi-cloud environments, ensuring legacy systems, human users, agents, cloud-based NHIs and service accounts are are secured with modern controls.
Discovery Capabilities
Universal Identity Visibility: Connects to the entire Identity and Access Management (IAM) stack (including Active Directory,cloud IdPs, SaaS, IaaS) to build a comprehensive view of all identities, including the often-overlooked Service Accounts (NHIs) and AI agents.Complete inventory and visual graph speeds understanding of relationships between users, identities and resources, surfacing overprivileged accounts and unnecessary licensing.
Exposure Analysis: Continuously scans the environment to uncover critical weaknesses, such as misconfigurations, insecure legacy authentication protocols (e.g., NTLMv1), and the presence of Shadow Admin accounts that are frequently exploited by groups like Scattered Spider.
Access Intelligence: Provides real-time, actionable context of access rights and permissions across all protected resources, eliminating blind spots in the identity attack path.
Protection Capabilities
Universal MFA Enforcement: Applies phishing-resistant Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Just-in-Time (JIT) access to systems and applications that natively lack protection, including command-line tools and legacy protocols, without requiring code changes.
Runtime Access Protection (RAP): Leverages patented inline architecture that acts as an Authentication Firewall and provides virtual fencing for service accounts to enforce security controls and deny high-risk access attempts in real-time, preemptively stopping attacks. Patented RAP also enables enforcement of Least Privilege access policies to control where each account can be used (‘virtual fencing’) and Just-In-Time (JIT) access at scale to achieve Zero Standing Privileges.
Legacy System Hardening: Secures all on-premises Active Directory assets and ensures compliance with modern security standards, mitigating the risk of lateral movement and credential harvesting against traditional infrastructure.
AI Agent Security: Ties every AI agent identity and actions to the initiating human for clear, immutable accountability and auditability. Inline security tools dynamically grants access between Al agents and MCP servers, restricting over-privileged access.
Privileged Access Security: Enforces Least Privilege access policies to control where each account can be used (‘virtual fencing’). Enforce Just-In-Time (JIT) access at scale to achieve Zero Standing Privileges
Defend Capabilities
Behavioral Threat Detection: Analyzes every authentication and access attempt using context and risk scoring to accurately detect malicious tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) for privilege escalation and lateral movement in real time.
Active Breach Containment: Provides immediate, granular control to block access at the authentication level, limiting the blast radius of an active breach and preventing attackers from using compromised credentials to move further across the network.
Service Account Protection: Enforces automated access policies on high-risk non-human identities (NHIs) to ensure they cannot be misused to access resources outside of their designated scope.
CrowdStrike
The CrowdStrike Falcon Platform delivers unified, AI-powered security that seamlessly integrates endpoint security, Cloud Security (CNAPP) and Cloud Identity Entitlement Management (CIEM), Continuous Threat and Exposure Management (CTEM), Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR), SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM), Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) and Modern Privileged Access to stop breaches in real-time, leveraging a single agent, single platform architecture.
Discovery Capabilities
Hybrid Identity Visibility: Provides comprehensive visibility across both on-premises Active Directory and cloud-based Identity Providers (IdPs) like Entra ID, unifying the security posture for hybrid identities.
SaaS Security Posture Management: Instantly connect 180+ SaaS apps to uncover misconfigurations, enforce governance, and gain actionable insights. Discover GPTs and Codex agents across SaaS platforms and map access, detect risky behavior, and contain threats in minutes.
Identity Store Exposure Management: Proactively scans identity stores to identify weaknesses such as compromised credentials, misconfigurations, and vulnerable service accounts, reducing the identity attack surface.
User and Entity Behavioral Analytics (UEBA): Establishes baselines for normal user and non-human identity (NHI) behavior to detect and analyze behavioral anomalies and potential insider threats.
Protection Capabilities
Continuous Access Evaluation Profile (CAEP): Continuously monitors user behavior and risk, dynamically enforcing adaptive controls such as revoking session tokens or forcing MFA re-authentication when risk levels change mid-session.
Falcon Privileged Access: Enforces Just-in-Time (JIT) access and Zero Standing Privileges for privileged roles, ensuring high-risk accounts only have the access they need, when they need it, directly mitigating the threat of privileged account takeover.
MFA Everywhere: Dynamically extends Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) coverage across the hybrid environment, including legacy systems and protocols, to stop attackers from using stolen credentials for initial access and lateral movement. CrowdStrike announced FalconID (GA in January) - phishing-resistant MFA built on FIDO2 standards as an option for customers who are looking for a strong platform approach as an alternative to leveraging disparate point solutions.
Defend Capabilities
Real-time ITDR: Detects identity attacks instantly, leveraging AI-powered anomaly detection to block suspicious access, including Active Directory reconnaissance and token-based attacks, before they escalate.
Integrated EDR & Identity: Correlates security events across the endpoint and identity to provide superior context and immediate, integrated response actions, ensuring the full attack path (from compromise to lateral movement) is blocked.
Managed Detection and Response (MDR): Offers 24/7 fully-managed identity protection via Falcon Complete, where expert human threat hunters utilize extensive threat intelligence (including TTPs of groups like Scattered Spider) to surgically respond to identity-based threats in minutes.
Real-Time CDR: Delivers real-time visibility of detections at the cloud control plane level and disrupts active cloud threats with automated, cloud-native responses to prevent breaches.
Research Methodology: This research by Software Analyst Cybersecurity Research (SACR) is based on proprietary analyst interpretation of data gathered through briefings, interviews, and surveys with market participants, cybersecurity leaders, practitioners and buyers. This report is for informational purposes only. Findings are valid only on the publication date due to the constantly changing technology landscape.






This is a great and well-researched read, even for those outside the cybersecurity space! Thanks for sharing :)
The shift from perimeter defense to identity-centric security is so critical right now. What stikes me most is how Scattered Spider exploits the weakest link which is often just human trust in voice calls. The point about needing behavior-based detection rather than just config audits really resonates. Traditional security tools simply cant keep up with attackers who move this fast and adapt in real time.