Securing the Identity Attack Surface: A Deep Dive into the New Battlefield of Identity Security
How identity leaders and enterprises can go about covering gaps and fully securing their identity attack surface
Introductory Blurb
Over the past two decades, the most successful identity security vendors—each nearing a billion in revenue—have been built around Identity Access Management (IAM), Identity Governance and Administration (IGA), and Privileged Access Management (PAM). This trend has given rise to giant leaders like Microsoft Identity, Okta, CyberArk, and SailPoint, with the latter poised for an IPO.
The next generation of identity security companies will unify IAM, PAM, and IGA, addressing the silos and security gaps that have emerged as enterprise stacks evolve with AI and LLMs. As organizations scale, identities—spanning both human and non-human identities (NHI)—has become one of the most exploited and overlooked attack surfaces in cybersecurity.
This report dissects the Identity Attack Surface, exposing how threat actors exploit identity weaknesses and what enterprises must do to defend against them.
Key Summary
The focus of this report: This report explores how enterprises can secure their identity attack surface using multiple approaches. I have written extensively on the identity governance ecosystem and non-human identities (NHIs). However, this report focuses on three key methodologies for how enterprises can go about monitoring, managing and securing their identity attack surface
Structure of the report: The rise of the identity attack is leading organizations to realize the importance of closing gaps within their existing identity solutions. This report aims to discuss how enterprises can leverage this 3-step process:
Visibility provides the foundational understanding of the identity landscape.
ISPM proactively enforces hygiene and proper configuration to reduce vulnerabilities.
ITDR actively monitors and mitigates threats as they arise, complementing proactive management strategies.
Why Identity?
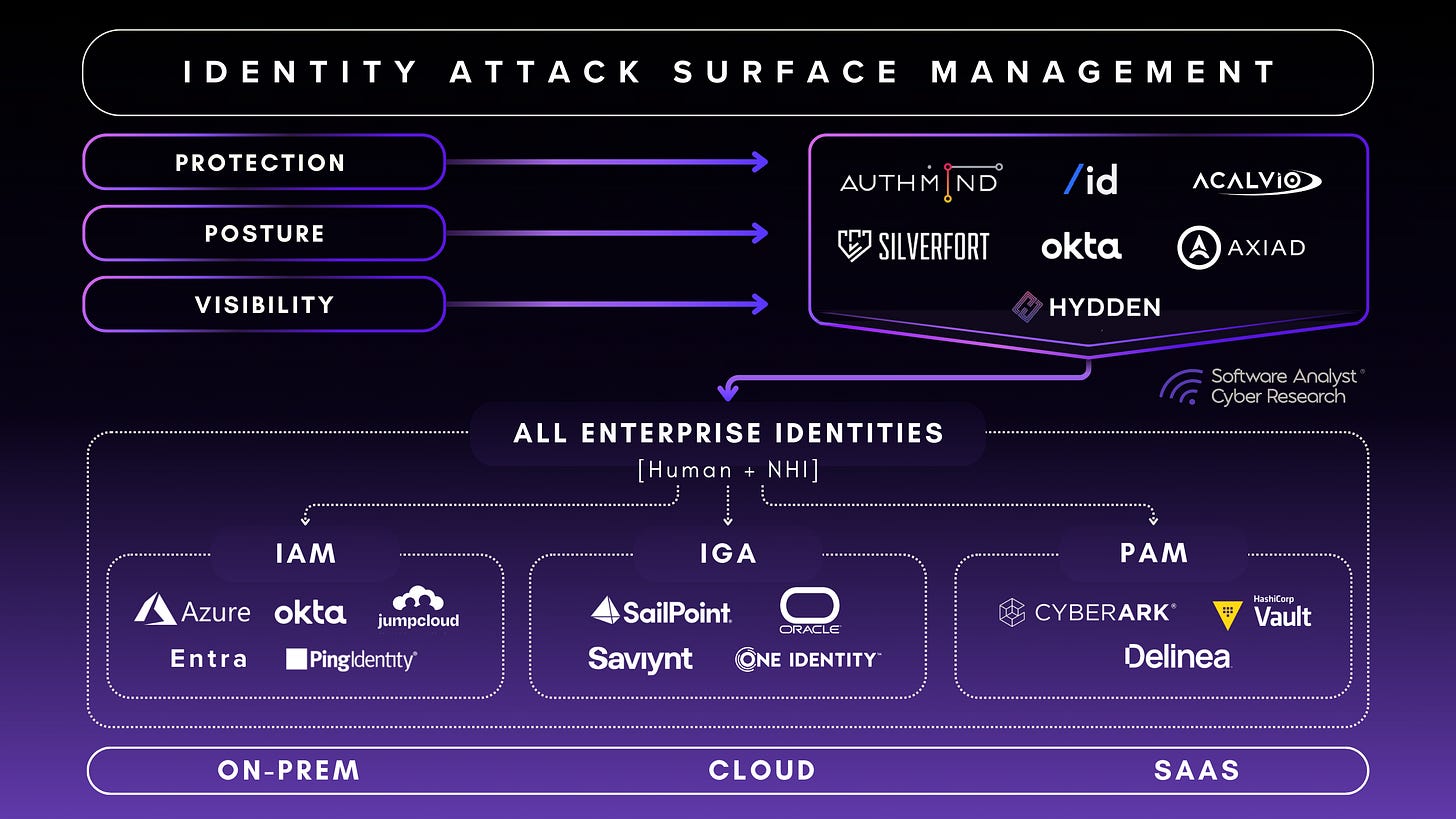
Why The Identity Attack Surface? The concept of an attack surface has long been recognized in security. However, its application to identity security is a relatively recent development that is gaining momentum. Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM) has emerged as a response to the growing realization of gaps within legacy identity vendors. The objective is to provide enterprises with full visibility into their legacy identity stacks, enforce posture controls, protect identities and drive remediation efforts based on informed insights.
How IASM is the next battlefront in Identity security: Over the past decade, organizations have focused primarily on managing access control (IAM), identity governance (IGA), and privilege management (PAM) solutions. These solutions hold a vast number of identities, yet they all provide very different solutions across a wide spectrum of architectures. These solutions don’t easily integrate amongst each other. This has led to organizations to have silos and many failed identity projects, resulting in numerous breaches. The next platform in security will have strong visibility, posture and protection mechanism.
The frequency and prevalence of identity attacks have surged over the years, due to weaknesses in identity systems, emphasizing the need for IASM. Attackers are increasingly leveraging techniques that bypass existing controls, forcing enterprises to adopt more advanced security measures.
90% of organizations experienced an identity-related breach in the past year, with 93% of these breaches being preventable through improved controls.
37% of organizations reported that implementing MFA for all users helped prevent or mitigate the effects of incidents. Other effective measures included regular reviews of access to sensitive data (42%) and privileged access (50%).
The MITRE ATT&CK framework reveals that 50% of observed attack tactics in the wild target identity, emphasizing the necessity for unified security visibility.
75% of detections are malware-free (a malware-free attack enables adversaries to operate under the radar and navigate seamlessly across endpoint and cloud domains).
Key report takeaways: Stronger visibility empowers organizations to take proactive, coordinated remediation steps. By breaking down silos between security teams, organizations can adopt the most secure and future-proof strategies to remediate vulnerabilities.
Identity security problem is a data problem: Identity security fundamentally hinges on data integrity. Despite frameworks like OCSF, IPSIE, and CAEP improving interoperability, they fail to fully normalize and correlate identity data across HR systems, traditional IAM solutions, and cloud-native identity platforms. This fragmentation weakens security postures, making enterprises vulnerable to identity-based threats. Organizations must proactively establish a unified identity data foundation, ensuring seamless correlation and governance. As these standards evolve, enterprises that prioritize structured identity data management will be better positioned to enhance security and streamline compliance.
Key representative vendors are discussed and highlighted throughout this report. These vendors represent this market ecosystem and the evolution toward visibility, posture and protection. There are many more vendors on the market that provide something similar or adjacent. One of the most successful has been CrowdStrike's achievement of $400M+ in revenue in less than 4+ years after their acquisition of Prempt in 2020. However, SACR selected these vendors after thorough product review and collaborated with them to successfully bring the research to market.
Siloed Gaps In Identities Today
What you see is just the beginning—beneath the surface, enterprises manage thousands of hidden identities, from users to non-human entities, each a potential attack vector. At the surface, enterprises rely on IAM, PAM, and IGA to manage identities—but beneath, a vast, fragmented web of disparate identities remains unseen. Service accounts, API keys, machine identities, shadow IT, and ephemeral credentials operate in the dark, expanding the Identity Attack Surface beyond traditional controls. Without visibility into these hidden layers, organizations are exposed to silent threats lurking below the surface.
The Modern Attack Surface Is Identity-Centric
To help us better understand the role of identity in the modern attack surface. We need to dissect and analyze — both:
Identity security management
Attack surface management
Let’s begin with breaking down identity into its foundational principles.
An identity is any entity within an enterprise that can be authenticated and authorized to perform actions within an IT system. We have two primary categories:
Human Identities ("People")
Non-Human Identities ("Machines")
Modern identity security management should takes a holistic approach, ensuring that both human and non-human identities are properly authenticated, authorized, and monitored to prevent unauthorized access, privilege abuse, and identity-based threats. It encompasses three critical areas:
Human identities, including employees, contractors, and partners, who require strong authentication, least privilege access, and governance to mitigate risks like credential theft and insider threats.
Non-human identities (NHIs), such as service accounts, bots, and API keys, that often have excessive privileges and require robust secrets management, rotation policies, and machine identity protection to prevent exploitation.
Digital identities, which include user accounts, roles, permissions, and credentials that define access and are susceptible to privilege escalation, misconfigurations, and sprawl if not properly managed.
Modern identity ecosystem continues to expand.
The identity ecosystem continues to explode and grow, as can be seen in the market map below:
I have written extensively on the identity governance ecosystem and non-human identities (NHIs). However, we want to delve into the attack surface built around this ecosystem today.
Attack Surface Management (ASM)
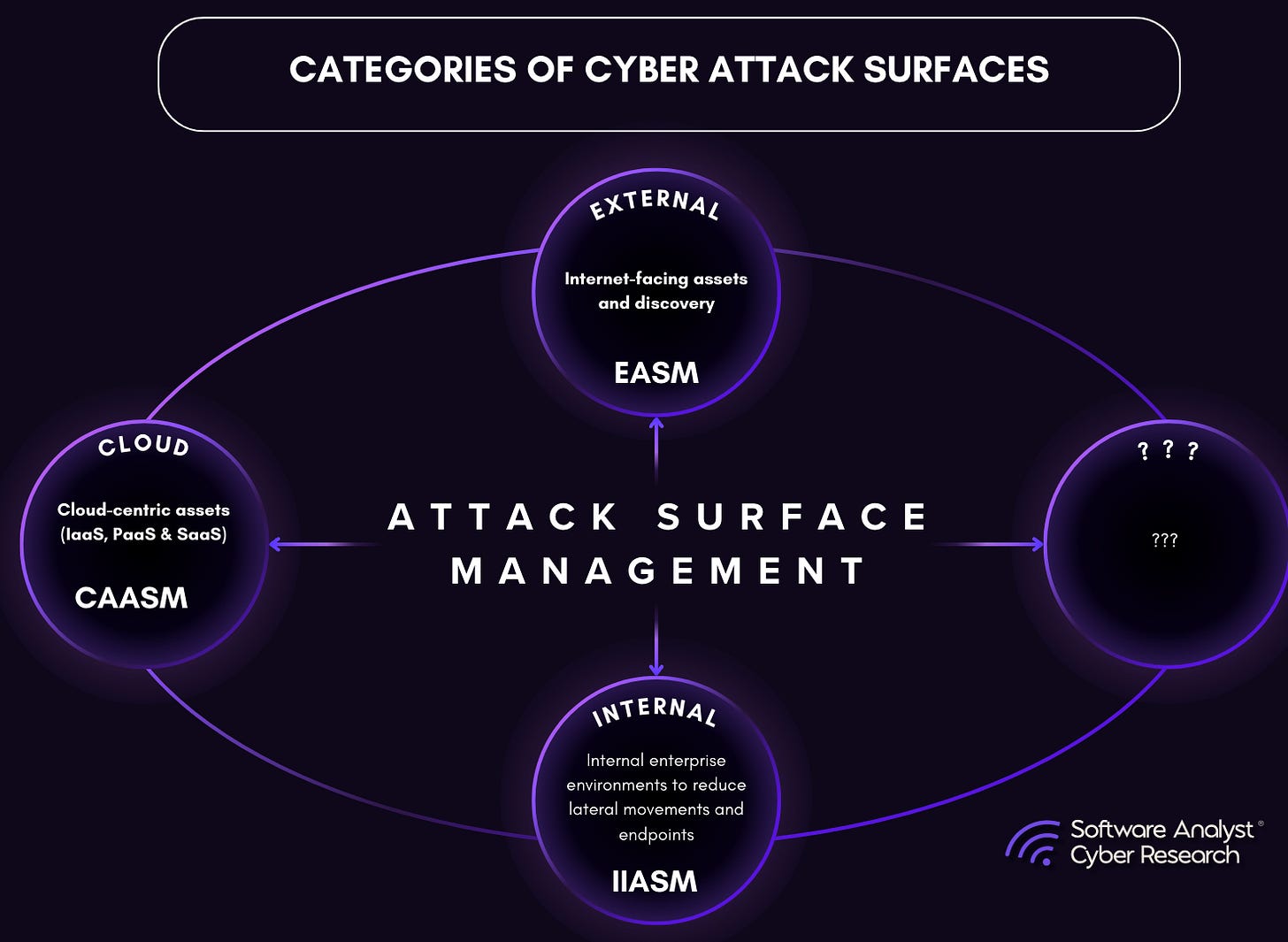
Attack Surface Management (ASM) involves the continuous discovery, inventorying, classification, and risk assessment of an organization's digital assets to minimize exposure to potential cyberattacks. It includes identifying all external and internal points that could be exploited by attackers, understanding their vulnerabilities, and taking proactive steps to secure them. Historically, ASM has been categorized into the following types:
EASM (External Attack Surface Management): Focuses primarily on internet-facing assets for a company, continuously discovering and monitoring misconfigurations, shadow IT, and vulnerabilities to minimize external exposure.
Traditional ASM (Attack Surface Management): Focuses on internal networks, endpoints, and identities, detecting insider threats, lateral movement risks, and unpatched vulnerabilities to strengthen internal security.
CAASM (Continuous Attack Surface Management): Provides a unified, real-time view of an organization’s entire attack surface by integrating security tools, prioritizing risks, and automating remediation.
Bringing It Together: Identity Centric (ASM)
After reviewing the key identity categories, it is evident that a significant portion of modern enterprise architecture is identity-driven across both human and machine identities. Traditional Attack Surface Management (ASM) focused on external and internal assets such as servers, applications, cloud environments, and endpoints. However, identity has become the primary attack vector in modern cyber threats, cutting across all boundaries. Additionally, Identity is the new perimeter i.e. Traditional ASM focused on networks and endpoints, but in cloud and hybrid environments, attackers bypass these and directly target credentials, privileges, and identity misconfiguration.
Credential stuffing, phishing, session hijacking, and privilege escalation attacks are now dominant in modern breaches (e.g., Okta and Uber breaches).
For example, Identity-based attacks have become central to the MITRE ATT&CK framework, with nearly half of its tactics relying on exploiting identity vulnerabilities. From initial access via credential theft to privilege escalation, persistence, and lateral movement, adversaries increasingly target weak authentication, excessive permissions, and mismanaged identities. Credential Access, a tactic entirely identity-focused, highlights the growing risk of stolen, cracked, or intercepted credentials. Attackers leverage identity-based reconnaissance, adversary-in-the-middle attacks, and privilege abuse to compromise organizations at scale. As identity becomes the new perimeter, SOC teams must integrate Identity Risk Management (IdRM) and Identity Threat Detection & Response (ITDR) to map and mitigate these attack vectors in real-time. Strengthening identity security is critical to closing gaps before they can be exploited.
Key parallels between traditional ASM and identity attack surface management (IASM) include :
Asset Discovery → Identity Discovery: Just as ASM maps exposed IT assets, IASM maps identities and their entitlements across cloud, SaaS, and on-prem environments.
Attack Path Analysis → Identity Risk Analysis: Traditional ASM traces exploitable attack paths; while IASM maps identity attack paths to identify privilege escalation risks.
Continuous Monitoring → Identity Drift & Exposure: ASM tracks asset changes, whereas IASM monitors identity and permission changes to prevent unintended exposure.
Introducing Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM)
IASM is the process of discovering, monitoring, and managing all identity-related vulnerabilities and risks within an organization. As the attack surface expands with the addition of new employees and applications creating new identities, enterprises struggle to manage them effectively, increasing the likelihood of attacks. Identity ASM or IASM extends visibility into identities, making ASM more holistic and adaptive to modern threats.
The end goal of IASM is to proactively limit exposure by preventing unauthorized users from compromising identities and gaining access. Just as ASM solutions analyze potential attack paths and identify key targets attackers may pursue, IASM provides centralized visibility into all identities, wherever they exist, focusing on securing identity-related assets against exploitation.
Use Cases
IASM cuts across traditional boundaries by:
Providing complete coverage of the identity lifecycle, identifying configuration states and hygiene across all identity types (B2E, B2C, Machine).
Enforcing security policies across solutions to align security policies across all existing products.
Proactively identifying threats early while offering holistic risk assessments.
Detecting exposed credentials, risky access patterns, and potential identity-based attack vectors that malicious actors could exploit.
Identifying dormant accounts, excessive privileges, and exposed credentials across cloud services, third-party applications, and development environments.
Prioritizing and resolving identity-based risks based on identity data source context and telemetry.
Existing Identity Security Frameworks
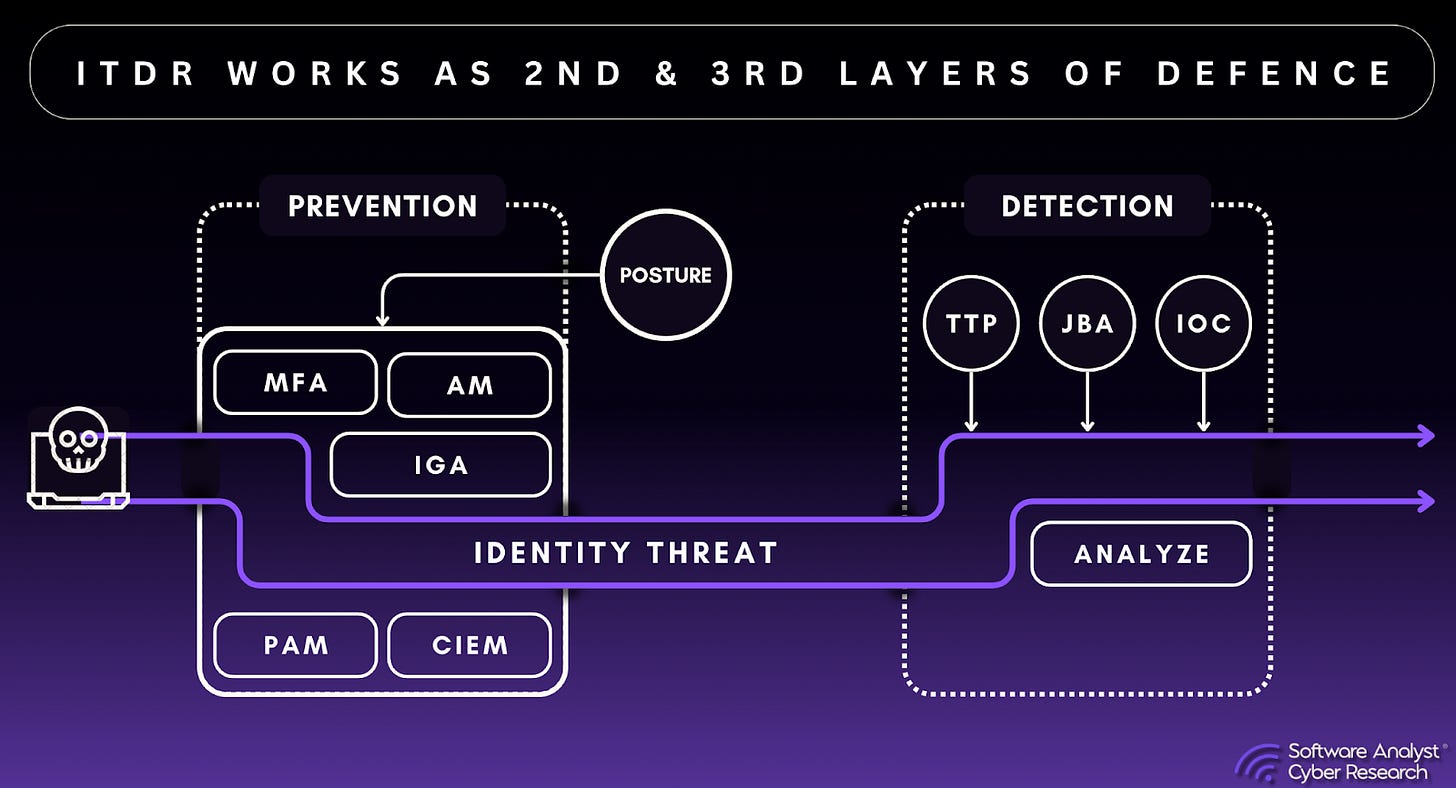
Prevention, detection and response
As identity-based attacks have become the primary entry point for cyber threats, many industry frameworks emphasize prevention techniques, detection mechanisms, and response capabilities for a comprehensive identity security strategy. While these frameworks collectively help reduce attack surfaces, more structured approaches are needed to address identity-specific threats.
IASM interconnects with existing identity categories
Many existing identity solutions focus on isolated aspects of identity security:
IAM, which focuses on the authentication layer
IGA, which focuses on account lifecycle management
PAM, which focuses on privileged users, secrets, and vaulting
While traditional IAM tools offer some identity management capabilities, they often operate in isolation and have significant limitations. Modern identity security requires a more comprehensive approach. Traditional solutions face several key challenges: they cannot effectively aggregate and normalize identity data across diverse platforms, they lack enterprise-wide contextual awareness for informed remediation, and they cannot provide standardized risk assessments across the organization. Most importantly, they fail to provide a holistic view of an organization's identity attack surface and cannot effectively prioritize identity-related risks that could lead to major security breaches.
Most of these solutions remain siloed, focused solely on the key areas they were designed to protect. IASM serves as a foundational layer that spans IAM, IGA, PAM, and ZTNA, enabling teams to take remediation actions and strengthen existing identity security implementations.
The fundamental identity security problem is a data problem. Despite efforts to improve interoperability through frameworks like OCSF, RISC, IPSIE, and CAEP, a significant gap remains in the identity security landscape. While these standards facilitate some integration between IAM systems, they lack the comprehensive capabilities needed to fully normalize and correlate identity data across the modern enterprise ecosystem, which spans human resources systems, traditional IAM solutions, and cloud-native identity management platforms. As these frameworks and standards gain traction in the industry, organizations will be required to comply. To maintain a strong security posture, they must also adopt the right technologies to secure all identities within their infrastructure, ensuring every identity is properly managed and protected.
Components of IASM
Discovery and visibility
Posture and hygiene
Protection and remediation
Discovery & Visibility
Visibility is the foundational pillar of IASM, as you cannot secure what you cannot see. Identity discovery and inventory are essential, as securing the attack surface depends on making all identities within an organization's ecosystem visible, including both human and non-human identities (NHIs).
The lack of identity visibility leads to shadow identities, orphaned accounts, over-privileged access, and an expanded attack surface. Visibility provides organizations with a real-time inventory of all identities, their relationships, and their associated permissions. Thus, visibility should encompass the following:
Discovering and identifying all human and machine identities to gain a clear, real-time view of who is accessing what resources.
Inventorying and cataloging identity types, permissions, and their associated attributes across all IT assets.
Mapping access privileges for each identity to enforce least-privilege principles and detect over-privileged accounts and unused permissions.
Mapping permissions and relationships: Understanding the relationships between identities and the assets they can access, such as cloud resources, applications, or data stores.
Ongoing and continuous monitoring of all identities, including new identities being created, rather than relying on static visibility, as most solutions on the market do.
The IASM process follows a comprehensive structured workflow, progressing from discovery to visibility and ultimately to controls. Unlike traditional static assessments, this approach ensures continuous, ongoing discovery across the enterprise's fragmented identity infrastructure. The system provides detailed reporting and dashboards for different stakeholders, all built on a unified data foundation that consolidates and analyzes all identity-related information.
Many of these solutions focus on:
Querying target systems and applications using their APIs
System and identity log parsing and analysis
Event-driven data capture
This data is then used to continuously monitor and track configuration and permission changes to detect identity-based threats.
Assessing Vendor’s Capabilities In Improved Identity Visibility
Comprehensive Identity Discovery: The first job of an IASM solution is to discover and ingest identity information from across the enterprise. This process requires integration with a wide range of systems where user identities and identity information are created, stored, and managed.
Example Case Study: Cloud Identity Exposure - A Fortune 500 company identified thousands of orphaned service accounts across its AWS and Azure environments. By leveraging automated identity discovery tools, it reduced its exposed attack surface by 40% in three months.
Breadth To Depth of integrations and connectors
The solution should integrate with various applications and services with strong connectors including:
Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) – Managing workforce identities and access.
Enterprise and Cloud Identity Directories – Centralized repositories for user authentication and authorization.
Traffic Monitoring & Directory Logs – Providing visibility into identity usage and anomalies.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) & Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) – Controlling and auditing privileged and general user access.
Identity Providers (IdPs) – Supporting digital identity management and single sign-on (SSO) across cloud-based and legacy on-premises environments.
Security & Networking Solutions – Including XDR, SASE, and other perimeter defense tools that integrate identity data for enhanced security.
SIEM & SOAR Platforms – Aggregating and correlating identity-related security events for threat detection and response.
Machine Identity Management Solutions – Governing non-human entities like bots, workloads, and service accounts.
Certificate Lifecycle Management Services – Ensuring the integrity and renewal of cryptographic credentials.
SaaS & API-Based Services – Extending identity governance across both cloud and on-premises applications
Identity scanning capabilities
An effective solution must:
Continuously monitor identities across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments.
Detect and inventory IAM accounts from providers like Microsoft, Okta, and JumpCloud.
Identify both human and non-human identities, including API keys, bots, and service accounts.
Uncover shadow identities and unauthorized access points, mitigating hidden risks within the identity attack surface.
Inventory of all identities
A comprehensive inventory of identities enables teams to:
Identify groups, departments, platforms, applications, and regions with the highest risks, helping determine root causes and prioritize resources effectively.
Normalize the data: Data normalization is essential for Identity and Risk Management (IdRM) solutions that integrate with various information sources. While systems like HRMS, enterprise directories, and PAM solutions may store user data differently (e.g., names, addresses, titles, business units, locations), normalization converts this into a standard format. This standardization is crucial for correlating, aggregating, and analyzing identity data across disparate sources.
Identity graph to correlate and map identity-to-asset relationships
To enhance visibility, organizations must be able to map which identities have access to which resources. Using graph-based security models, vendors should enable organizations to visualize identity-based attack paths and illustrate relationships between identities, groups, roles, entitlements, credentials, secrets, and other entities.
Leverage external standards for context: Solutions should integrate with industry frameworks and standards, including the Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework (OCSF), Risk Identification and Site Criticality Toolkit (RISC), and the Continuous Access Evaluation Protocol (CAEP). Additionally, emerging standards like the Interoperability Profile for Secure Identity in the Enterprise (IPSIE) should be considered.
Analyze and assign risk scores
Risk Scoring capabilities: Risk scoring capabilities are essential in identity security because they provide a quantifiable measure of the likelihood that an identity is compromised or poses a security risk. By assigning risk scores to users, service accounts, and access requests based on behavioral analytics, historical activity, and contextual factors, organizations can prioritize their security efforts. Risk scores enable the enforcement of dynamic, risk-based access controls. For example, a high-risk score could trigger additional authentication measures, limit privileges, or initiate automated incident response workflows, thereby reducing the chance for identity misuse.
Real-Time Identity Monitoring: A robust database should be able to scan, capture and map identities. This functionality helps organizations detect anomalies in login patterns, permission changes, and access behavior.
Detecting Orphaned & Unused Accounts: The system should also be able to perform regular audits and remove inactive accounts. It should also identify external identities (e.g., contractors, vendors) that no longer require access.
Visibility Can’t Be Static, But Constant
Visibility into identities must be continuous and dynamic, rather than static. Organizations need to implement scanning mechanisms that monitor repositories frequently, as new identities and development processes are continuously introduced. Continuous, automated account discovery capabilities are essential for detecting when new accounts are created. Some of these capabilities can be integrated with cloud providers to identify newly created identities.
Posture & Hygiene
This sub-category emphasizes maintaining a robust security baseline by assessing and improving the configuration and hygiene of identities. ISPM ensures that identities are correctly provisioned, regularly updated, and aligned with the principle of least privilege.
Challenges with IAM and Identity projects
Some of the major challenges in identity security can be tied to a perspective shared by Bojan Simic:
“Every major cybersecurity report clearly points out that authentication and identity verification attacks account for the vast majority of breaches. Unfortunately, we still see most InfoSec teams "taking the pill" by investing in more alerting and discovery of problems instead of truly working to get rid of the source of the problem. Sometimes this requires a bit of surgery. The good news is that phishing resistant authentication is deployable across all user groups within the enterprise. This can enable organizations to massively improve security and user experience. This will also help them achieve their Zero Trust/BeyondCorp identity assurance goals. - Full post here”
How to prevent identity issues - Key Components
Identity Misconfiguration Detection: Identifying issues such as overly permissive roles, weak passwords, and misaligned access policies.
Compliance and Governance: Ensuring that identities adhere to internal policies and regulatory requirements (e.g., NIST, GDPR, HIPAA).
Lifecycle Management: Regularly decommissioning stale or orphaned accounts to minimize exposure.
Access Reviews: Conducting periodic reviews to validate that permissions align with job roles.
Why Separate Visibility from Posture
Separating Visibility from Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) is crucial for effective identity security. This distinction allows organizations to thoroughly identify and understand their identity landscape and relationships (Visibility) first, before implementing security policies and controls (ISPM). Visibility focuses on discovery and awareness, providing a comprehensive understanding of all identities and their interconnections within the organization. Meanwhile, ISPM centers on governance and enforcement, ensuring the identity landscape remains secure by minimizing misconfigurations, enforcing least privilege access, and eliminating over-provisioning.
By prioritizing visibility, organizations can take proactive and coordinated remediation steps based on a deep understanding of their identity landscape. Breaking down silos between security teams fosters collaboration, leading to comprehensive solutions that provide secure and future-proof remediation actions.
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM)
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) has emerged as a critical approach for enterprises. ISPM is a proactive framework designed to enhance and maintain the security posture of an organization's identity infrastructure, preventing breaches and unauthorized access. It involves continuous monitoring and analysis of identities, access rights, and authentication processes across the entire digital ecosystem.
Similar to Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) but within an identity context, ISPM proactively identifies vulnerabilities and minimizes the identity attack surface for both human and non-human identities. Customers prioritize addressing known security gaps over-generalized threat detection due to concerns about noise and false positives. The insights from the visibility component should drive action to correct posture issues and fortify defenses against identity risks. Example Case Study: Preventing Overprivileged Access- A healthcare provider detected over 5,000 overprivileged accounts with access to sensitive patient data. After deploying an identity posture management solution, it reduced excessive permissions by 70%, mitigating the risk of insider threats.
How Organizations Should Fix Identity Posture & Hygiene Issues
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) provides organizations with a systematic approach to continuously assess, manage, and remediate identity risks. This ensures that security gaps are proactively addressed before they can be exploited. By integrating ISPM into their identity security strategy, organizations can automate access reviews, enforce least privilege policies, detect misconfigurations, and eliminate identity sprawl. ISPM strengthens authentication controls, monitors non-human identities, and implements risk-based access policies, ultimately reducing the attack surface and improving overall security posture.
With ISPM in place, organizations can effectively tackle the following identity hygiene challenges:
Detect & Fix Identity Misconfigurations: ISPM solutions help security teams proactively detect and fix identity misconfigurations that could lead to unintended privilege escalation or lateral movement. This includes identifying misconfigured IAM roles, overly permissive policies, and wildcard permissions that grant excessive access. Organizations should implement network segmentation strategies to prevent unauthorized identity access to sensitive assets unless explicitly required. Regular IAM audits uncover potential weaknesses before exploitation.
Strict Enforcement of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Mandatory MFA for all privileged and external accounts as well as for companies moving to implement stronger authentication processes is critical. Cybercriminals continuously exploit weak or stolen credentials, making MFA an essential safeguard against unauthorized access. Organizations should move beyond legacy MFA implementations and adopt passwordless authentication wherever possible to reduce the attack surface for phishing-based credential theft. As adversaries refine their tactics, adaptive authentication mechanisms that factor in risk-based signals should be prioritized.
Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): One of the most effective ways for organizations to strengthen their identity security posture is by enforcing the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP). Identity sprawl and over-permissioned accounts have made organizations vulnerable to privilege escalation attacks. Security teams must ensure that every identity—human or non-human—has only the necessary permissions required to perform its function, nothing more. Implementing just-in-time (JIT) access further minimizes standing privileges, reducing the risk of persistent overexposure. Dynamic access control frameworks, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC), should be leveraged to grant permissions based on contextual signals rather than static entitlements.
Managing, monitoring and reducing Identity Sprawl: Unchecked identity sprawl leads to thousands of unnecessary or duplicate accounts, increasing the attack surface. To mitigate this risk, enterprises should actively merge duplicate accounts, remove unused roles, and decommission inactive identities. Automated tools should continuously scan and flag over-provisioned accounts, ensuring access remains tightly controlled as business needs evolve.
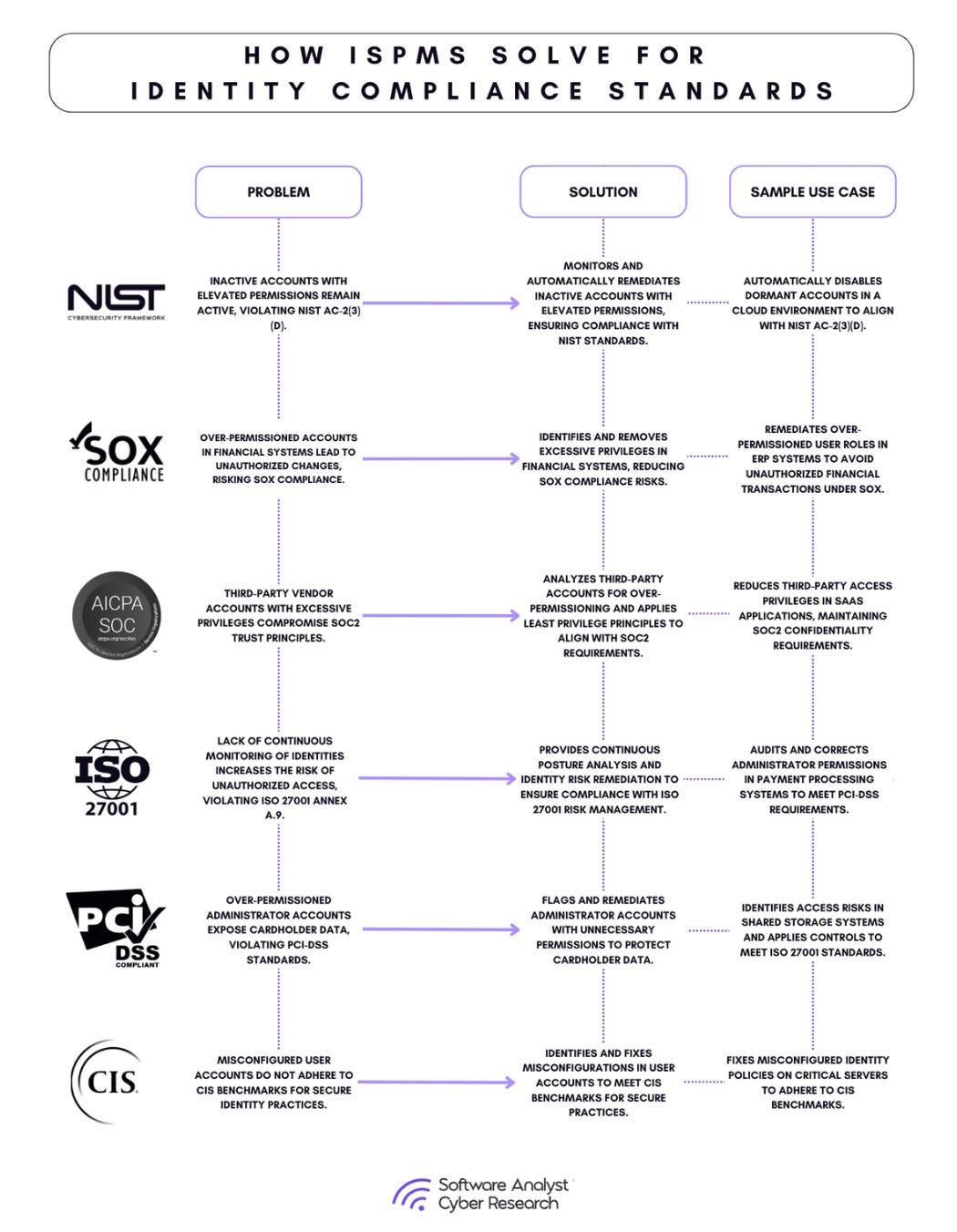
Case Study Outcomes for ISPM: Framework control mapping to the following frameworks
NIST - It could be linked to NIST AC-2(3)(d) to disable unused accounts or AC-2(11), AC-6-7 to remove unused permissions
There are other key compliance frameworks around SOX | SOC2 | PCI-DSS | ISO 27001 | CIS
Okta ISPM’s powered by its Spera acquisition has robust resources and capabilities around resolving ISPM compliance issues.
Protection and Remediation
Lateral movement case study
71% of ransomware attacks leverage credential access tactics, and more than 80% of cyberattacks involve compromised credentials. This makes lateral movement a common attack method, highlighting how attackers exploit stolen identities to move undetected across networks.
Even with visibility and strong identity hygiene, attackers continuously evolve their techniques to bypass security controls and compromise identities within enterprises. This underscores the importance of continuous monitoring of identities and their activities, as behavioral monitoring and anomaly detection enable early threat identification. These signals help administrators spot potential compromises early, triggering alerts when suspicious patterns emerge.
Lateral movement has become one of the most widely used techniques in cyberattacks. This method enables adversaries to escalate a localized breach into a full-scale organizational compromise. To counter this, enterprises must implement layered protection mechanisms. This report focuses on two major technologies for modern identity protection:
Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)
Deceptive technologies leveraging honeytokens
Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)
The reality is that traditional security solutions, such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Privileged Access Management (PAM), and network segmentation, have failed to stop lateral movement. These solutions either lack visibility into authentication activity or only protect privileged accounts, leaving standard user accounts vulnerable. Additionally, Active Directory (AD) inherently trusts valid credentials, making it unable to differentiate between a legitimate user and an attacker using stolen credentials. This fundamental limitation leaves organizations exposed to identity-based threats.
Enter ITDR. ITDR directly addresses these blind spots by continuously monitoring authentication requests, detecting anomalies in user behavior, enforcing real-time multi-factor authentication (MFA) verification, and blocking unauthorized access before attackers can pivot to additional resources. ITDR solutions analyze user behavioral anomalies, authentication protocol changes, and external risk signals to detect identity threats. Some solutions leverage IOCs, TTPs, MIT&RE framework and risk analysis to differentiate between normal and malicious activity. By integrating natively with IAM infrastructure, ITDR integrates directly with IAM and proactively blocks threats before access is granted. ITDR ensures comprehensive protection across all authentication protocols, including command-line access tools like PsExec and Remote PowerShell, which are frequently abused for lateral movement. Given that 24 billion compromised credentials are circulating on the dark web, proactively detecting and disrupting lateral movement attacks in real time is no longer optional—it is a necessity for a robust identity security strategy.
Additionally, MFA and ITDR work in tandem to enhance security. Strong MFA, supported by posture and hygiene solutions, allows ITDR to validate access attempts automatically, minimizing false positives and reducing the SecOps workload. With MFA, ITDR can block identity threats in real time, ensuring that only verified access attempts are allowed.
When selecting an Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) solution, organizations must evaluate its coverage, detection accuracy, and response capabilities. An effective ITDR platform should integrate seamlessly with all identity and access management (IAM) solutions, whether on-premises or in the cloud, ensuring comprehensive protection across Active Directory (AD), cloud identity providers (IdPs), VPNs, and SaaS applications. It must accurately identify a broad spectrum of identity threats, including credential theft, lateral movement, and privilege escalation, while offering real-time mitigation rather than relying solely on reactive alerts.
Real-time threat detection leverages machine learning and anomaly detection to identify unusual authentication patterns, such as impossible travel logins, credential stuffing attacks, and unauthorized lateral movement within hybrid environments. Behavioral analytics for high-privilege accounts further enhance security by continuously monitoring privileged user sessions and enforcing risk-based conditional access controls.
Deceptive technologies and ITDR
Deceptive technologies, such as honeytokens and honey accounts, play a critical role in Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) by providing early detection of identity-related attacks. Enterprises leverage deception to protect identities across on-premises and multi-cloud environments, addressing key gaps in traditional ITDR approaches.
Traditional detection methods struggle to distinguish between legitimate and malicious usage of valid accounts, leaving blind spots in Active Directory (AD) logs, domain controllers, and endpoint detection response (EDR) systems. Attackers frequently exploit stolen credentials, including SAML/JWT tokens and offline attacks like Kerberoasting, as well as emerging zero-day identity threats that bypass conventional security measures. By deploying deceptive identities within credential caches and creating honey accounts, organizations can lure adversaries into revealing their presence without relying solely on log correlation.
The NSA and Five Eyes intelligence agencies recommend honeytokens as an effective strategy for detecting AD compromises, as they provide strong indicators of unauthorized access. Vendors like Acalvio’s Identity Protection enhance ITDR by deploying honeytokens that remain attractive to attackers while integrating seamlessly with security operations. This approach extends beyond AD to multi-cloud environments, where identity remains a top attack vector. Cloud-based adversaries increasingly exploit IAM misconfigurations, API-based attacks, and privilege escalation techniques to gain unauthorized access.
More enterprises are deploying honeytoken traps alongside their ITDR solutions. Honeytokens in cloud environments—including IAM roles and deceptive access keys—provide real-time threat intelligence by alerting security teams to unauthorized activity before an attack escalates. For example, CrowdStrike partners with Acalvio to enable comprehensive ITDR with a defense-in-depth strategy that combines traditional detection methods with deception technology. Their autonomous deception farms simplify deployment at scale, securing enterprises with thousands of endpoints and complex identity environments. A real-world case study highlights how a honeytoken exposed a malicious insider who attempted to manipulate user provisioning scripts—an attack that bypassed other security controls but was immediately detected through deception.
Remediation Capabilities
Effective remediation is a critical component of identity protection, ensuring that detected threats do not escalate into full-blown security breaches.
Remediation is the final and often most important step in the security process, encompassing visibility, posture, and protection. All identity security technologies should incorporate strong remediation capabilities. Upon detecting an identity compromise, an automated incident response mechanism should take immediate action, such as locking compromised accounts, triggering step-up authentication via MFA, and integrating with SOC and SIEM platforms for threat correlation and response orchestration. For ITDR vendors, sending alerts to a SIEM or data lake is often considered table stakes. Additionally, forensic analysis and post-incident reporting play a critical role in strengthening identity security by providing detailed audit logs that allow security teams to investigate attack patterns and proactively mitigate future risks.
For example, in a real-world ITDR deployment, a financial institution’s security system detected an unauthorized administrator login attempt from a foreign location at 5 AM. The ITDR platform immediately flagged the anomaly, triggered an automated account lockdown, and enforced MFA re-authentication, effectively preventing a privilege escalation attack. Other key aspects of an effective ITDR response include automated threat containment and security posture adjustments, as discussed earlier. Upon detecting a suspicious authentication attempt, ITDR solutions must immediately disrupt active identity threats through mechanisms like session termination, universal logout, and privilege revocation. This case highlights how ITDR’s real-time monitoring, automation, and identity analytics enable organizations to proactively block identity-based attacks before they escalate.
Beyond immediate mitigation, ITDR also enhances long-term security posture by feeding threat intelligence back into identity hygiene and risk management practices. It enables organizations to reduce the IAM attack surface by revoking excessive permissions, adjusting role-based access, and ensuring continuous identity monitoring.
Identity Attack Surface Representative Vendors
Visibility & Posture
Hydden
Axiad
Silverfort
Protection & Remediation
Silverfort
Authmind
SlashID
Acalvio
Note: this isn’t a fully holistic list of hundreds of vendors providing adjacent solutions, but a few vendors selected as representative vendors.
REPRESENTATIVE VENDORS: POSTURE & PROTECTION PLATFORM
Silverfort - Advanced Posture & Protection Platform
With identity-based attacks surging, the need for real-time visibility, adaptive authentication, and automated enforcement has never been greater. Silverfort built strong foundations—helping enterprises secure their IAM infrastructure in real-time across different stacks, but primarily within active directory and enabling timely enforcements through multi-factor authentication for the prevention of unauthorized access.
They have further extended the platform from threat detection and response over the years to cover multiple areas, including agentless universal MFA and privilege access management (PAM). The next iteration of their platform is leveraging their strengths to extend real-time visibility, risk-based authentication, and dynamic policy enforcement across an organization’s entire identity infrastructure. They have expanded successfully into the ISPM category to emphasize discovery and continuous discovery on static risks. Because Silverfort integrates directly into the IAM infrastructure, they have visibility into every authentication, creating a complete visibility foundation for ISPM, and more specifically identity threat exposure management. This naturally complements their ITDR real-time capabilities.
Traditional IAM solutions often stop at authentication, leaving security teams with visibility but no real enforcement capability. Silverfort changes this by actively blocking risky authentication attempts and enforcing security controls at the identity layer. Security teams can:
Automatically apply Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for high-risk identities (workforce, non-human, privileged, etc).
Block insecure authentication requests before they reach critical systems.
Restrict access based on real-time risk assessments and behavioral indicators
Silverfort’s platform enables custom policy-driven enforcement, allowing security teams to apply MFA selectively based on privilege levels or risky user behavior.
How Rezonate Expands Silverfort’s Reach into Cloud IAM
Silverfort has long excelled in on-prem AD accounts and built some good capabilities for cloud identities. Hybrid environments create identity fragmentation—all of which traditional IAM solutions struggle to address. With Rezonate’s cloud-native identity capabilities, Silverfort now extends its visibility, monitoring and real-time enforcement model into multi-cloud environments, SaaS applications, and hybrid IAM ecosystems — eliminating any blind spots. This applies to both human and non-human identities (NHIs).
Silverfort (powered by Rezonate), enables security teams to detect and respond to cloud identity threats in real time, identifying privilege escalation attempts, lateral movement tactics, and misconfigurations before they can be exploited. The integration allows Silverfort to enforce risk-based policies at every authentication layer—whether on-prem, in AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure—ensuring identity security remains continuous and adaptive.
This integration is already proving effective in stopping real-world identity threats. One notable case from the transcript describes how an enterprise used Silverfort’s deny access policy—enabled by Rezonate—to block an attempted privilege escalation attack. The attacker attempted to exploit NTLM v1 authentication, a legacy protocol that attackers commonly target for credential relay attacks. Silverfort, with Rezonate’s cloud visibility, correlated the authentication request with cloud-based identity activity, identifying anomalous privilege access behavior. In real-time, the platform enforced a deny policy, stopping the attacker before they could escalate privileges and move laterally across the environment.
Silverfort’s convergence of ITDR and ISPM creates a unified, defense layer, enabling organizations to identify risky configurations while also detecting, mitigating, and preventing identity threats in real-time—before they turn into full-scale breaches. This positions Silverfort as one of the leaders in this market paving the way for a new standard in proactive identity threat prevention and posture management.
REPRESENTATIVE VISIBILITY VENDORS
Hydden: Identity Focused On Identity Surface Protection
Hydden is an emerging vendor with strong capabilities in enhancing the visibility and discovery of all identities across existing identity solutions today. They focus on identity attack surface management by mapping non-human identities (NHI) and human identities across the enterprise. Hydden helps organizations identify orphaned accounts, misconfigured identities, and security gaps in multi-cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments.
The system automates threat detection and risk scoring based on predefined security rules and frameworks (e.g., NIST CSF v2.0). Users can classify identity risks on a scale from 1 to 10 and customize them based on historical threats (e.g., password spraying, orphaned accounts).
Risk Classification & Threat Scoring
Dynamic risk scoring, identified earlier in the report, is critical for successful vendors that produce outcome driven results. Hydden showed an impressive capability around assigning contextual identity risk scores, classifying identities based on exposure, misconfigurations, and access patterns.
This enhances threat modeling capabilities by prioritizing security responses based on attack likelihood and impact. If an anomaly is detected, the system flags suspicious activity, such as unauthorized travel logins or excessive permissions. Hydden’s risk engine not only assigns a threat score but also provides confidence levels and contextual relationships (e.g., linking identities to SaaS applications, AD entitlements, and MFA status).
Hydden & CyberArk Partnership
Hydden recently struck a partnership with CyberArk for privileged access management (PAM) and vaulting credentials.
Hydden enhances CyberArk Privileged Access Manager (PAM) by providing 100% visibility into the entire identity attack surface. By creating a unified data layer, Hydden continuously tracks and analyzes identity security posture and threat indicators, ensuring that every privileged identity is securely managed, vaulted, and monitored in real time. With Hydden’s privileged identity discovery, CyberArk customers can automatically detect and vault all accounts that should be, but are not yet, secured within CyberArk Safes.
CyberArk Privileged Access customers utilize this analysis to ensure every identity is securely managed and continuously monitored for any external changes by Hydden. A few notable things from this partnership include:
Automated Account Classification – Hydden classifies privileged accounts (e.g., accounts ending in tagged as Dual Admin Accounts) to determine if they should be vaulted
Human & Non-Human Visibility & Mapping – Hydden provides full context and risk scoring for every account, aiding in connecting CyberArk users, machine accounts, and service identities to their rightful owners. This also aids in simplifying vaulting decisions.
Security Hygiene & Risk Assessment – Hydden identifies orphaned, stale, and compromised accounts, as well as privileged identities with no MFA or excessive entitlements.
What stood out as a key advantage of this integration is Hydden’s ability to discover accounts across platforms, systems, and applications that typically fall outside CyberArk's standard discovery scope. Beyond PAM, Hydden provides the "visibility foundation" for IGA, PAM, and security platforms. They have built extensive integrations across multi-cloud & hybrid environments.
Automation and Remediation
Hydden integrates with automated security response workflows, allowing for trigger-based automation (e.g., automatically flagging and deactivating an account based on security violations). The platform automates identity posture management and alerts users to pending MFA setups, misconfigurations, and suspicious activities.
Axiad - Leading Identity Risk Management
Axiad Security, a well-established credential management company, has strategically expanded its capabilities into Identity-Driven Risk Management (IdRM)—a category it helped define. IdRM which is built into Axiad Mesh enables security and identity teams to collaboratively manage identity risks. This approach revolves around three core pillars:
Identifying identity-related risks
Quantifying those risks to prioritize remediation,
Fortifying identities against both current and future threats.
Axiad’s comprehensive framework provides a methodology for organizations to proactively manage identity risks at scale. A deeper breakdown of this approach is available in their in-depth IdRM report.
Axiad’s Axiad Mesh solution has emerged as a key player, bridging the gap between Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) and Identity Threat Detection & Response (ITDR). At the core of Axiad’s competitive differentiation is its applied risk quantification and scoring engine, which provides a comprehensive evaluation of identity-related threats. By integrating advanced risk modeling, the platform offers insights into:
The blast radius of compromised identities – Understanding how identity vulnerabilities propagate across systems.
Business impact assessment – Evaluating the significance of identity risks based on the roles, permissions, and systems affected.
These are key objectives for identity leaders and teams when evaluating the health of their identity systems. Additionally, Axiad helps identify profiling gaps in identity access across IDP, IGA, and PAM solutions. These capabilities allow identity teams to quantify the actual security impact of identity risks, enabling enterprises to shift from static security postures to a risk-prioritized approach to identity security.
Axiad distinguishes itself with strong visualization and risk analytics capabilities. Its bubble chart and dashboard views provide security teams with a clear, high-level overview of identity risks segmented by geography, business unit, and application. This real-time, intuitive interface makes it significantly easier for CISOs, security analysts, and identity teams to understand, contextualize, and act on identity risks. Given increasing regulatory and compliance demands—including NIST 800-63, CIS Controls, GDPR, and SOC 2—Axiad’s risk-scoring model provides a valuable advantage, helping enterprises meet governance requirements while enhancing overall security posture.
Axiad’s IDRM solution is uniquely positioned at the intersection of ISPM, which focuses on improving identity hygiene and security posture, ensuring that organizations enforce strong authentication mechanisms, eliminate misconfiguration gaps and provide enterprises with proactive security solutions.
REPRESENTATIVE PROTECTION & POSTURE VENDORS
AuthMind: Identity Security Through Observability
AuthMind approaches the challenge of ISPM and ITDR with an observability-centric approach rather than static rule enforcement. Its identity access graph correlates network traffic with identity events, providing organizations with a real-time, contextual understanding of access—not just who is accessing what, but how they are doing it.
This approach allows AuthMind to uncover identity blind spots (shadow assets, missing MFA, unauthorized local accounts), surface hygiene issues, and identity infrastructure gaps (compromised identities, brute-force attacks, etc.) and detect shadow and suspicious activities, security bypasses, privileged access control violations, MFA circumventions and more. The full context of identity infrastructure—what is happening, why, and how to manage it—is critical for efficiently identifying and rapidly remediating identity-related risks and threats.
With extensive experience from major network security firms like Palo Alto Networks and McAfee, the AuthMind team emphasizes integrating network flow traffic, cloud flow traffic, and identity events, correlating them to provide a fully contextualized view of all identities and access paths. The platform is built on an underlying infrastructure that collects vast amounts of data and enriches it with machine learning.
Identity Observability as the Core Pillar
Identity observability is built around tracking who is accessing what, when, and how - by monitoring access flows across networks, cloud, and SaaS apps. Instead of relying solely on logs and pre-set policies, AuthMind has built their architecture around analyzing access paths—showing whether a user bypassed MFA, avoided VPN controls, or accessed assets in an unusual way. The platform features an identity access flow graph that continuously analyzes access paths across human, machine, managed, and unmanaged identities. By correlating network, identity, and cloud events, AuthMind provides real-time insights into identity behaviors that traditional IAM and security tools often miss. Its strong access graph capabilities are further validated by its patented technology (US Patent 11,895,144 B2), which covers continuous identity access flow mapping.
Solving the “Blind Spot”
Most organizations have shadow identities, orphaned accounts, and unmanaged credentials that create significant blind spots in their security posture. AuthMind’s ISPM automatically identifies and remediates these hidden risks, detecting privilege escalation attempts, misconfigured MFA policies, and unauthorized service account usage.
AuthMind goes beyond merely recording login events—they illustrate the actual sequence of actions taken by identities, helping teams understand how threats emerge. This also enables machine learning models to analyze access trends over time, detecting anomalies in human vs. non-human identity behaviors. AuthMind offers a holistic view of identity posture, hygiene, and threats. This removes the need for siloed identity security tools by integrating observability, security posture management, and threat detection into a single platform.
AuthMind’s observability-first approach is compelling. The real test will be whether enterprises recognize observability as an essential component of identity security. Ultimately, the platform aims to eliminate identity blind spots and provide deeper, contextualized visibility across all identities.
The platform integrates with major identity providers (Okta, Active Directory, Ping, OneLogin), SIEM solutions (Splunk, IBM QRadar, Exabeam), network security tools (Zscaler, SASE, VPNs), and endpoint security platforms (CrowdStrike, SentinelOne). One notable success story involves a large North American environmental services provider with thousands of employees, which faced critical identity security challenges, including shadow access, MFA inconsistencies, unmanaged SaaS applications, and ongoing enumeration attacks targeting Active Directory administrators. By deploying the AuthMind Platform, the company achieved enterprise-wide observability, identified thousands of MFA misconfigurations, detected and stopped real-time identity threats, and secured over 300 high-risk user identities. Recognized as a Gartner Cool Vendor in 2022, AuthMind continues to expand its presence as a critical identity security solution provider.
REPRESENTATIVE PROTECTION VENDORS
Acalvio Security: Proactive Detection with Honey Tokens
Acalvio’s innovation lies in its ability to create and deploy honey tokens dynamically and at scale. These fake credentials, service accounts, and access keys are designed to look indistinguishable from real assets within an organization’s identity ecosystem. Their purpose is simple: when accessed or interacted with, they immediately signal malicious intent.
How It Works:
Automated Honey Token Deployment: Using AI-driven automation, Acalvio generates honey tokens tailored to an organization’s unique environment. These tokens mimic real accounts, adhering to naming conventions and attributes specific to the target system, be it Active Directory (AD) or cloud identities platforms like AWS IAM or Azure AD.
Placement Across Identity Layers:
AD and On-Premises: Fake service accounts, shadow admins, and privileged user profiles are created to trap attackers exploiting AD vulnerabilities.
Endpoints: Tokens are embedded in credential caches like Windows RDP, browser sessions, and authentication vaults.
Cloud Identity Systems: Deceptive IAM users, roles, and API keys are deployed across AWS, Azure, and GCP environments to detect unauthorized cloud activity.
High-Fidelity Alerts: Any interaction with these tokens triggers an immediate, actionable alert, eliminating the noise of false positives. Security teams can respond confidently, knowing the alert signals malicious activity.
Case Study
In one instance, Acalvio helped a large enterprise thwart an insider threat. A rogue IAM team member, leveraging legitimate access, used a provisioning server to disable user accounts in Active Directory. Despite employing traditional security tools like PAM, EDR, and AD log analytics, the organization failed to detect the malicious activity.
Acalvio’s deception platform, however, had planted honey tokens within AD. When the rogue insider attempted to disable one of these deceptive accounts, an alert was triggered, allowing the organization to intercept the attack before significant damage occurred. This proactive detection not only prevented a potential disaster but highlighted a critical gap in traditional security approaches.
Integrations
Acalvio’s success is amplified through its strategic partnerships with CrowdStrike and Microsoft:
CrowdStrike Falcon Identity Protection: Honey token alerts integrate seamlessly into CrowdStrike’s console, requiring no additional agents or software deployment. This partnership ensures rapid adoption and streamlined detection.
Microsoft Defender for Identity (MDI): Similarly, Acalvio integrates with MDI, automating honey token creation and enabling detection within Microsoft’s native security tools.
These integrations make deception technology easily accessible, reducing operational overhead for enterprises and enabling security teams to receive high-fidelity alerts within their existing management consoles. Recognizing the shift toward cloud-native environments, Acalvio has also extended its honey token methodology to protect multi-cloud identity systems.
Why Deception Matters for Identity Security
Deception technology offers a distinct advantage: it does not rely on prior knowledge of attacker tactics or techniques. Instead, it targets the attacker’s goals—using traps designed to expose malicious intent. In an era where attackers leverage generative AI like DeepSeek to develop novel techniques, deception provides a preemptive layer of security that complements traditional detection methods.
As highlighted by NSA and Gartner research, deception is no longer optional—it is a critical component of the modern security stack and an essential pillar of Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR). Acalvio’s honey token methodology offers a proactive, scalable, and high-fidelity approach to securing identity attack surfaces. Traditional defenses, such as log-based detection and network traffic inspection, falter against sophisticated identity attacks. Offline attacks like Kerberoasting or Silver Ticket exploits operate outside the visibility of SIEM tools, while insider threats—cloaked in legitimate permissions—bypass anomaly-based detection.
SlashID
SlashID is one of the earliest vendors in this market and offers some of the strongest capabilities for securing the identity attack surface, particularly through posture management and real-time threat detection for non-human identities (NHIs). The platform provides visibility into both human and machine identities, with particularly strong features for cloud environments.
Designed to identify security posture issues and active threats as they emerge, SlashID continuously streams identity-related logs and event data to detect unfolding threats. By leveraging AI-driven anomaly detection, the platform identifies suspicious activities, such as unauthorized privilege escalations, lateral movement across cloud environments, and NHI misuse.
With a centralized control panel, SlashID provides cross-environment visibility, allowing security teams to manage identities and monitor security events across multiple cloud providers and identity providers (IdPs). Its customizable policy frameworks and remediation APIs are designed around security detections and automated responses, reducing the mean time to detection and remediation. Additionally, SlashID’s architecture prevents mass exfiltration of sensitive data by encrypting user information with unique keys derived from a hardware security module (HSM)-backed master, ensuring robust data protection.
Mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK framework, SlashID’s customizable detection framework enables organizations to fine-tune security rules based on their risk tolerance and compliance requirements. The platform integrates seamlessly with SIEM and SOAR solutions, ensuring that security teams receive high-fidelity alerts without excessive noise. By proactively monitoring and detecting identity-based threats in real time, SlashID helps enterprises mitigate breaches before they escalate, making it a crucial component of modern ITDR strategies.
Key Capabilities:
Emphasis on real-time: SlashID provides real-time event streaming, posture management, and automated remediation, enabling organizations to detect and mitigate identity-based threats. The platform continuously streams identity event logs in real time, detects anomalies as they occur, and offers cross-environment visibility for monitoring identities across cloud providers, IdPs, and on-prem infrastructure. SlashID’s behavioral anomaly detection capabilities continuously monitor identity usage patterns to detect deviations that may indicate credential compromise or privilege escalation attempts. While early, there are some good features around automated threat responses that implement real-time remediation workflows, such as session termination, forced MFA reauthentication, or dynamic access restrictions.
Identity Posture Management & Compliance Alignment: SlashID effectively identifies misconfigurations, excessive permissions, and dormant accounts that could be exploited by attackers that map security risks to compliance frameworks.
Securing Non-Human Identities (NHIs): SlashID extends protection beyond human users to API keys, service accounts, and machine identities, reducing risks associated with automated processes and CI/CD pipelines. They detect unauthorized API token misuse, preventing attackers from leveraging compromised credentials to move laterally across cloud environments.
Adaptive Access Controls & Zero Trust Integration: SlashID enforces adaptive access policies based on risk scores, forcing reauthentication or revoking access when anomalies are detected. Its risk scoring capabilities continuously evaluate identity posture, behavioral deviations, and external threat intelligence and helps distinguish between normal and suspicious activities. Indicators such as excessive permissions, unusual login patterns, privilege escalation, and compromised credentials dynamically adjust risk scores, triggering adaptive security measures which ultimately ensures threats are detected instantly.
Appendix: (I)
Adjacent Competitive Landscape
This is a market map ecosystem that explores more vendors that provide similar and adjacent capabilities across the ecosystem.
Appendix: (II)
Honourable mentions:
Okta’s Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM):, Okta strengthened its ISPM capabilities with the acquisition of Spera Security in December 2023, providing a proactive approach to securing the identity attack surface. Positioned as a layer above IAM components like IGA and PAM, ISPM focuses on reducing identity-related risks before breaches occur. A key differentiator of Okta’s ISPM is its unified approach to human and NHIs, providing visibility into API key security, service account governance, and non-human identity risks. By incorporating Spera’s insights, Okta’s ISPM now extends beyond identity providers to SaaS applications and cloud infrastructures such as AWS, Salesforce, and GitHub, helping organizations efficiently detect and remediate security gaps. Okta’s ISPM is positioning itself as an essential layer in identity security, offering multi-layered defense capabilities across access management, posture insights, and risk-based remediation.
JumpCloud acquired stack identity: JumpCloud’s acquisition of Stack Identity marked a significant expansion of its ITDR and ISPM capabilities. Stack Identity’s platform originally integrated ITDR, ISPM, CIEM, and SaaS entitlements, continuously monitoring data risks and vulnerabilities stemming from compromised identities, credentials, and unauthorized privileges. A key feature was its dynamic discovery and inventory capabilities, which automatically detect and map cloud data stores, identifying identity, access, and application connections in real time. By integrating Stack Identity’s advanced data analytics technology, JumpCloud enhances its ability to detect unmonitored and unauthorized access pathways, a critical gap in traditional IAM solutions. The acquisition also accelerates JumpCloud’s capability to process and act on billions of identity signals, ensuring organizations can proactively mitigate identity-related threats before they escalate.
Delinea acquired Authomize for its excellence in multi-platform visibility, entitlement tracking, and ITDR, leveraging graph-based analytics to detect identity threats across cloud and SaaS environments. The acquisition was driven primarily by Authomize’s broad coverage, particularly in Active Directory—a core strength that enables integration with multiple identity providers to identify misconfigurations and automate remediation. While Delinea focuses on privileged access security, vaulting, and behavioral monitoring to ensure proper management of privileged accounts, Authomize enhanced Delinea’s capabilities by improving vaulting processes and enforcing security posture. This alignment with Delinea’s PAM capabilities strengthened secure credential storage and automated privilege control. Ultimately, Authomize contributed significantly to Delinea’s visibility and detection improvements.
Appendix: (III)
ISPM vs IGA: How is it different from IGA?
Many industry practitioners are familiar with IGA. Some of the key components for what IGA does.
Conclusion: The Future of Identity Attack Surface Management
As the digital landscape continues to expand, identity has become the new perimeter in cybersecurity. The rise of non-human identities, the increasing complexity of multi-cloud environments, and the acceleration of identity-based attacks demand a more holistic and proactive approach to security.
This report highlights that Visibility, ISPM, and ITDR form the foundation of a resilient identity security strategy. Visibility ensures organizations understand their attack surface, ISPM enforces proper security hygiene to minimize risk, and ITDR provides real-time detection and response to evolving threats. Together, these elements create a robust defense mechanism that adapts to modern identity-driven threats.
Going forward, organizations must embrace automation, AI-driven analytics, and continuous identity monitoring to stay ahead of attackers. Identity security is no longer just an IT function—it is a business imperative that impacts regulatory compliance, operational resilience, and trust. By prioritizing Identity Attack Surface Management, enterprises can significantly reduce the risk of identity compromise, privilege abuse, and supply chain attacks, ensuring that their most critical assets—identities—remain secure in an increasingly interconnected world.